HBO1 HAT complexes target chromatin throughout gene coding regions via multiple PHD finger interactions with histone H3 tail
- PMID: 19187766
- PMCID: PMC2677731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.007
HBO1 HAT complexes target chromatin throughout gene coding regions via multiple PHD finger interactions with histone H3 tail
Abstract
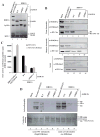
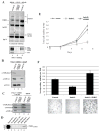
The HBO1 HAT protein is the major source of histone H4 acetylation in vivo and has been shown to play critical roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. A distinctive characteristic of HBO1 HAT complexes is the presence of three PHD finger domains in two different subunits: tumor suppressor proteins ING4/5 and JADE1/2/3. Biochemical and functional analyses indicate that these domains interact with histone H3 N-terminal tail region, but with a different specificity toward its methylation status. Their combinatorial action is essential in regulating chromatin binding and substrate specificity of HBO1 complexes, as well as cell growth. Importantly, localization analyses on the human genome indicate that HBO1 complexes are enriched throughout the coding regions of genes, supporting a role in transcription elongation. These results underline the importance and versatility of PHD finger domains in regulating chromatin association and histone modification crosstalk within a single protein complex.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Multifunctional acyltransferase HBO1: a key regulatory factor for cellular functions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 14;29(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00661-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39543485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The scaffolding protein JADE1 physically links the acetyltransferase subunit HBO1 with its histone H3-H4 substrate.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 23;293(12):4498-4509. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000677. Epub 2018 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29382722 Free PMC article.
-
Exchange of associated factors directs a switch in HBO1 acetyltransferase histone tail specificity.Genes Dev. 2013 Sep 15;27(18):2009-24. doi: 10.1101/gad.223396.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 24065767 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Jade-1 in the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) HBO1 complex.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 24;283(43):28817-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801407200. Epub 2008 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18684714 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering structure, function and mechanism of lysine acetyltransferase HBO1 in protein acetylation, transcription regulation, DNA replication and its oncogenic properties in cancer.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Feb;77(4):637-649. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03296-x. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31535175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Jade-1S phosphorylation induced by CK1α contributes to cell cycle progression.Cell Cycle. 2016;15(8):1034-45. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1152429. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 26919559 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of gene expression dynamics by co-transcriptional histone methylations.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Apr 28;49(4):e326. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.19. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28450734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional acyltransferase HBO1: a key regulatory factor for cellular functions.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 Nov 14;29(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00661-y. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39543485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HBO1 is required for the maintenance of leukaemia stem cells.Nature. 2020 Jan;577(7789):266-270. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1835-6. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31827282
-
New connections between ubiquitylation and methylation in the co-transcriptional histone modification network.Curr Genet. 2021 Oct;67(5):695-705. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01196-x. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 34089069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avvakumov N, Cote J. The MYST family of histone acetyltransferases and their intimate links to cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:5395–5407. - PubMed
-
- Consortium TEP. The ENCODE (ENCyclopedia Of DNA Elements) Project. Science. 2004;306:636–640. - PubMed
-
- Doyon Y, Cayrou C, Ullah M, Landry AJ, Cote V, Selleck W, Lane WS, Tan S, Yang XJ, Cote J. ING tumor suppressor proteins are critical regulators of chromatin acetylation required for genome expression and perpetuation. Mol Cell. 2006;21:51–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

