APE1/Ref-1 interacts with NPM1 within nucleoli and plays a role in the rRNA quality control process
- PMID: 19188445
- PMCID: PMC2655621
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01337-08
APE1/Ref-1 interacts with NPM1 within nucleoli and plays a role in the rRNA quality control process
Abstract
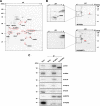
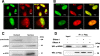
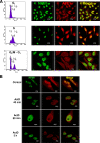
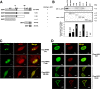
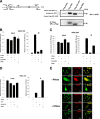
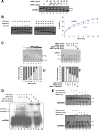
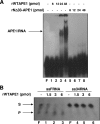
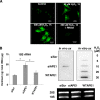
APE1/Ref-1 (hereafter, APE1), a DNA repair enzyme and a transcriptional coactivator, is a vital protein in mammals. Its role in controlling cell growth and the molecular mechanisms that fine-tune its different cellular functions are still not known. By an unbiased proteomic approach, we have identified and characterized several novel APE1 partners which, unexpectedly, include a number of proteins involved in ribosome biogenesis and RNA processing. In particular, a novel interaction between nucleophosmin (NPM1) and APE1 was characterized. We observed that the 33 N-terminal residues of APE1 are required for stable interaction with the NPM1 oligomerization domain. As a consequence of the interaction with NPM1 and RNA, APE1 is localized within the nucleolus and this localization depends on cell cycle and active rRNA transcription. NPM1 stimulates APE1 endonuclease activity on abasic double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) but decreases APE1 endonuclease activity on abasic single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) by masking the N-terminal region of APE1 required for stable RNA binding. In APE1-knocked-down cells, pre-rRNA synthesis and rRNA processing were not affected but inability to remove 8-hydroxyguanine-containing rRNA upon oxidative stress, impaired translation, lower intracellular protein content, and decreased cell growth rate were found. Our data demonstrate that APE1 affects cell growth by directly acting on RNA quality control mechanisms, thus affecting gene expression through posttranscriptional mechanisms.
Figures


References
-
- Andersen, J. S., Y. W. Lam, A. K. L. Leung, S. E. Ong, C. E. Lyon, A. I. Lamond, and M. Mann. 2005. Nucleolar proteome dynamics. Nature 43377-83. - PubMed
-
- Apicelli, A. J., L. B. Maggi, Jr., A. C. Hirbe, A. P. Miceli, M. E. Olanich, C. L. Schulte-Winkeler, A. J. Saporita, M. Kuchenreuther, J. Sanchez, K. Weilbaecher, and J. D. Weber. 2008. A non-tumor suppressor role for basal p19ARF in maintaining nucleolar structure and function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 281068-1080. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beernink, P. T., B. W. Segelke, M. Z. Hadi, J. P. Erzberger, D. M. Wilson III, and B. Rupp. 2001. Two divalent metal ions in the active site of a new crystal form of human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, Ape1: implications for the catalytic mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 3071023-1034. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa, A., and E. G. Moss. 2003. RNA repair: damage control. Curr. Biol. 13R482-R484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
