Phytol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice
- PMID: 19188468
- PMCID: PMC2838495
- DOI: 10.1177/0192623308330789
Phytol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice
Abstract
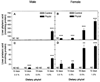
Phytanic acid is a branched-chain, saturated fatty acid present in high concentrations in dairy products and ruminant fat. Some other dietary fats contain lower levels of phytol, which is readily converted to phytanic acid after absorption. Phytanic acid is a peroxisome proliferator binding the nuclear transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) to induce expression of genes encoding enzymes of fatty acid oxidation in peroxisomes and mitochondria. Administration of dietary phytol (0.5% or 1%) to normal mice for twelve to eighteen days caused consistent PPARalpha-mediated responses, such as lower body weights, higher liver weights, peroxisome proliferation, increased catalase expression, and hepatocellular hypertrophy and hyperplasia. Female mice fed 0.5% phytol and male and female mice fed 1% phytol exhibited midzonal hepatocellular necrosis, periportal hepatocellular fatty vacuolation, and corresponding increases in liver levels of the phytol metabolites phytanic acid and pristanic acid. Hepatic expression of sterol carrier protein-x (SCP-x) was five- to twelve-fold lower in female mice than in male mice. These results suggest that phytol may cause selective midzonal hepatocellular necrosis in mice, an uncommon pattern of hepatotoxic injury, and that the greater susceptibility of female mice may reflect a lower capacity to oxidize phytanic acid because of their intrinsically lower hepatic expression of SCP-x.
Figures






References
-
- Atshaves BP, Petrescu A, Starodub O, Roths J, Kier AB, Schroeder F. Expression and intracellular processing of the 58 kDa sterol carrier protein 2/3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase in transfected mouse L-cell fibroblasts. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:610–622. - PubMed
-
- Atshaves BP, Storey SM, Petrescu A, Greenberg CC, Lyuksyutova OI, Smith R, 3rd, Schroeder F. Expression of fatty acid binding proteins inhibits lipid accumulation and alters toxicity in L cell fibroblasts. Am J Physiol. 2002;283:C688–C703. - PubMed
-
- Atshaves BP, Payne HR, McIntosh AL, Tichy SE, Russell D, Kier AB, Schroeder F. Sexually dimorphic metabolism of branched chain lipids in C57BL/6J mice. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:812–830. - PubMed
-
- Atshaves BP, McIntosh AL, Payne HR, Mackie J, Kier AB, Schroeder F. Effect of branched-chain fatty acid on lipid dynamics in mice lacking liver fatty acid binding protein gene. Am J Physiol. 2005;288:C543–C558. - PubMed
-
- Atshaves BP, McIntosh AL, Landrock D, Payne HR, Mackie JT, Maeda N, Ball J, Schroeder F, Kier AB. Effect of SCP-x gene ablation on branched-chain fatty acid metabolism. Am J Physiol. 2007;292:G939–G951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

