Disentangling prenatal and inherited influences in humans with an experimental design
- PMID: 19188591
- PMCID: PMC2634805
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0808798106
Disentangling prenatal and inherited influences in humans with an experimental design
Abstract
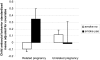
Exposure to adversity in utero at a sensitive period of development can bring about physiological, structural, and metabolic changes in the fetus that affect later development and behavior. However, the link between prenatal environment and offspring outcomes could also arise and confound because of the relation between maternal and offspring genomes. As human studies cannot randomly assign offspring to prenatal conditions, it is difficult to test whether in utero events have true causal effects on offspring outcomes. We used an unusual approach to overcome this difficulty whereby pregnant mothers are either biologically unrelated or related to their child as a result of in vitro fertilization (IVF). In this sample, prenatal smoking reduces offspring birth weight in both unrelated and related offspring, consistent with effects arising through prenatal mechanisms independent of the relation between the maternal and offspring genomes. In contrast, the association between prenatal smoking and offspring antisocial behavior depended on inherited factors because association was only present in related mothers and offspring. The results demonstrate that this unusual prenatal cross-fostering design is feasible and informative for disentangling inherited and prenatal effects on human health and behavior. Disentangling these different effects is invaluable for pinpointing markers of prenatal adversity that have a causal effect on offspring outcomes. The origins of behavior and many common complex disorders may begin in early life, therefore this experimental design could pave the way for identifying prenatal factors that affect behavior in future generations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barker DJP. Mothers, Babies, and Health in Later Life. Edinburgh, UK: Churchill Livingston; 1998.
-
- Bateson P, et al. Developmental plasticity and human health. Nature. 2004;430:419–421. - PubMed
-
- Vaessen N, et al. Association between genetic variation in the gene for insulin-like growth factor-I and low birthweight. Lancet. 2002;359:1036–1037. - PubMed
-
- Kaaja RJ, Greer IA. Manifestations of chronic disease during pregnancy. J Am Med Assoc. 2005;294:2751–2757. - PubMed
-
- Ray JG, Vermeulen MJ, Schull MJ, Redelmeier DA. Cardiovascular health after maternal placental syndromes (CHAMPS): Population-based retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2005;366:1797–1803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

