Fibronectin-based isolation of valve interstitial cell subpopulations: relevance to valve disease
- PMID: 19189392
- PMCID: PMC4396829
- DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.32382
Fibronectin-based isolation of valve interstitial cell subpopulations: relevance to valve disease
Abstract
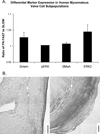
Myxomatous mitral valves (MVs) contain elevated proportions of unique cell populations such as myofibroblasts. Without a reliable technique to isolate such cell populations, however, it has been difficult to study the role of these cells. The goal of this study was to use fibronectin (FN) to isolate distinct cell subpopulations from normal porcine MVs. Cells from porcine posterior MV leaflets were separated based on time-dependent adhesion to either tissue culture plastic (TCP) flasks or FN-coated flasks. The resultant "FAST" and "SLOW" adhering subpopulations from each technique were phenotyped using flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry to detect expression of myofibroblast markers, enzymes for collagen synthesis, and MAP kinases. Compared with FN SLOW, FN FAST showed significantly higher expression of prolyl 4-hydroxylase, heat shock protein-47 (HSP47), smooth muscle alpha-actin (SMalphaA), nonmuscle myosin (Smem), extracellular-related signaling kinase (ERK) 1, ERK2, and phosphorylated-ERK. In contrast, TCP FAST showed higher expression of only HSP47, SMalphaA, and Smem compared with TCP SLOW. In conclusion, differential adhesion to FN successfully separated a myofibroblast-like subpopulation from the posterior leaflet of the MV. This subpopulation may be useful in studying myxomatous MV disease, although additional studies remain to verify that this myofibroblast-like population resembles that observed in myxomatous MV disease.
Figures





References
-
- Hewitson T, Martic M, Darby I, Kelynack K, Bisucci T, Tait M, Becker G. Intracellular cyclic nucleotide analogues inhibit in vitro mitogenesis and activation of fibroblasts derived from obstructed rat kidneys. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2004;96(2):e59–e66. - PubMed
-
- Florquin S, Rouschop K. Reciprocal functions of hepatocyte growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta1 in the progression of renal diseases: a role for CD44? Kidney Int Suppl. 2003;86:S15–S20. - PubMed
-
- Wynes M, Frankel S, Riches D. IL-4-induced macrophage-derived IGF-I protects myofibroblasts from apoptosis following growth factor withdrawal. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76(5):1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Gómez J, Molero X, Vaquero E, Alonso A, Salas A, Malagelada J. Vitamin E attenuates biochemical and morphological features associated with development of chronic pancreatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287(1):G162–G169. - PubMed
-
- Rabkin E, Aikawa M, Stone JR, Fukumoto Y, Libby P, Schoen FJ. Activated interstitial myofibroblasts express catabolic enzymes and mediate matrix remodeling in myxomatous heart valves. Circulation. 2001;104(21):2525–2532. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

