A Cytosolic Homomerization and a Modulatory Domain within STIM1 C Terminus Determine Coupling to ORAI1 Channels
- PMID: 19189966
- PMCID: PMC2659200
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C800229200
A Cytosolic Homomerization and a Modulatory Domain within STIM1 C Terminus Determine Coupling to ORAI1 Channels
Abstract
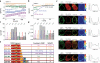
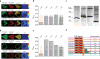
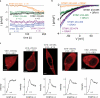
In immune cells, generation of sustained Ca(2+) levels is mediated by the Ca(2+) release-activated Ca(2+) (CRAC) current. Molecular key players in this process comprise the stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) that functions as a Ca(2+) sensor in the endoplasmic reticulum and ORAI1 located in the plasma membrane. Depletion of endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) stores leads to STIM1 multimerization into discrete puncta, which co-cluster with ORAI1 to couple to and activate ORAI1 channels. The cytosolic C terminus of STIM1 is sufficient to activate ORAI1 currents independent of store depletion. Here we identified an ORAI1-activating small fragment (OASF, amino acids 233-450/474) within STIM1 C terminus comprising the two coiled-coil domains and additional 50-74 amino acids that exhibited enhanced interaction with ORAI1, resulting in 3-fold increased Ca(2+) currents. This OASF, similar to the complete STIM1 C terminus, displayed the ability to homomerize by a novel assembly domain that occurred subsequent to the coiled-coil domains. A smaller fragment (amino acids 233-420) generated by a further deletion of 30 amino acids substantially reduced the ability to homomerize concomitant to a loss of coupling to as well as activation of ORAI1. Extending OASF by 35 amino acids (233-485) did not alter homomerization but substantially decreased efficiency in coupling to and activation of ORAI1. Expressing OASF in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL) mast cells demonstrated its enhanced plasma membrane targeting associated with 2.5-fold larger CRAC currents in comparison with the complete STIM1 C terminus. In aggregate, we have identified two cytosolic key regions within STIM1 C terminus that control ORAI1/CRAC activation: a homomerization domain indispensable for coupling to ORAI1 and a modulatory domain that controls the extent of coupling to ORAI1.
Figures
References
-
- Berridge, M. J., Bootman, M. D., and Roderick, H. L. (2003) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4 517–529 - PubMed
-
- Hoth, M., and Penner, R. (1992) Nature 355 353–356 - PubMed
-
- Lewis, R. S., and Cahalan, M. D. (1990) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 52 415–430 - PubMed
-
- Parekh, A. B., and Putney, J. W., Jr. (2005) Physiol. Rev. 85 757–810 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

