Intramembrane proteolysis by signal peptide peptidases: a comparative discussion of GXGD-type aspartyl proteases
- PMID: 19189970
- PMCID: PMC2682845
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R800040200
Intramembrane proteolysis by signal peptide peptidases: a comparative discussion of GXGD-type aspartyl proteases
Abstract
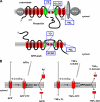
Intramembrane-cleaving proteases are required for reverse signaling and membrane protein degradation. A major class of these proteases is represented by the GXGD-type aspartyl proteases. GXGD describes a novel signature sequence that distinguishes these proteases from conventional aspartyl proteases. Members of the family of the GXGD-type aspartyl proteases are the Alzheimer disease-related gamma-secretase, the signal peptide peptidases and their homologs, and the bacterial type IV prepilin peptidases. We will describe the major biochemical and functional properties of the signal peptide peptidases and their relatives. We then compare these properties with those of gamma-secretase and discuss common mechanisms but also point out a number of substantial differences.
Figures

References
-
- Wolfe, M. S., and Kopan, R. (2004) Science 305 1119–1123 - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. S., Ye, J., Rawson, R. B., and Goldstein, J. L. (2000) Cell 100 391–398 - PubMed
-
- Kopan, R., and Ilagan, M. X. (2004) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5 499–504 - PubMed
-
- Haass, C., and Steiner, H. (2002) Trends Cell Biol. 12 556–562 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

