Functional characterization of tlmK unveiling unstable carbinolamide intermediates in the tallysomycin biosynthetic pathway
- PMID: 19189972
- PMCID: PMC2659183
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M900640200
Functional characterization of tlmK unveiling unstable carbinolamide intermediates in the tallysomycin biosynthetic pathway
Abstract
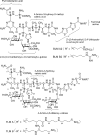
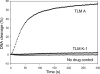
Tallysomycins (TLMs) belong to the bleomycin family of anticancer antibiotics. TLMs differ from bleomycins primarily by the presence of a 4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-l-talose sugar attached to C-41 as part of a glycosylcarbinolamide. We previously proposed, on the basis of bioinformatics analysis of the tlm biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158, that the tlmK gene is responsible for the attachment of this sugar moiety. We now report that inactivation of tlmK in S. hindustanus abolished TLM A and TLM B production, the resultant DeltatlmK mutant instead accumulated five new metabolites, and introduction of a functional copy of tlmK to the DeltatlmK mutant restored TLM A and TLM B production. Two major metabolites, TLM K-1 and TLM K-2, together with three minor metabolites, TLM K-3, TLM K-4, and TLM K-5, were isolated from the DeltatlmK mutant, and their structures were elucidated. These findings provide experimental evidence supporting the previous functional assignment of tlmK to encode a glycosyltransferase and unveil two carbinolamide pseudoaglycones as key intermediates in the TLM biosynthetic pathway. TlmK stabilizes the carbinolamide intermediates by glycosylating their hemiaminal hydroxyl groups, thereby protecting them from hydrolysis during TLM biosynthesis. In the absence of TlmK, the carbinolamide intermediates fragment to produce an amide TLM K-1 and aldehyde intermediates, which undergo further oxidative fragmentation to afford carboxylic acids TLM K-2, TLM K-3, TLM K-4, and TLM K-5.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of tlmH in Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insight into tallysomycin biosynthesis and affording a novel bleomycin analog.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Feb;6(2):349-56. doi: 10.1039/b918106g. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20094654 Free PMC article.
-
The tallysomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insights into the biosynthesis of the bleomycin family of antitumor antibiotics.Mol Biosyst. 2007 Jan;3(1):60-74. doi: 10.1039/b615284h. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Mol Biosyst. 2007. PMID: 17216057
-
Improved production of the tallysomycin H-1 in Streptoalloteichus hindustanus SB8005 strain by fermentation optimization.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 May;86(5):1345-53. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2406-9. Epub 2010 Jan 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20049429
-
Comparative analysis of the biosynthetic gene clusters and pathways for three structurally related antitumor antibiotics: bleomycin, tallysomycin, and zorbamycin.J Nat Prod. 2011 Mar 25;74(3):526-36. doi: 10.1021/np1008152. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Nat Prod. 2011. PMID: 21210656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biosynthetic gene cluster for the anticancer drug bleomycin from Streptomyces verticillus ATCC15003 as a model for hybrid peptide-polyketide natural product biosynthesis.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Dec;27(6):378-85. doi: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000194. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11774003 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: an update for 2009-2010.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015 May-Jun;34(3):268-422. doi: 10.1002/mas.21411. Epub 2014 May 26. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2015. PMID: 24863367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered production and evaluation of 6'-deoxy-tallysomycin H-1 revealing new insights into the structure-activity relationship of the anticancer drug bleomycin.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017 Aug 23. doi: 10.1038/ja.2017.93. Online ahead of print. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 28831149
-
A designer bleomycin with significantly improved DNA cleavage activity.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Aug 15;134(32):13501-9. doi: 10.1021/ja3056535. Epub 2012 Aug 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22831455 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of tlmH in Streptoalloteichus hindustanus E465-94 ATCC 31158 unveiling new insight into tallysomycin biosynthesis and affording a novel bleomycin analog.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Feb;6(2):349-56. doi: 10.1039/b918106g. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20094654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawaguchi, H., Tsukiura, H., Tomita, K., Konishi, M., and Saito, K. (1977) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 30 779–788 - PubMed
-
- Konishi, M. S. K., Numata, K., Tsuno, T., and Asama, K. (1977) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 30 789–805 - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., and Stubbe, J. (2005) Nat. Rev. Cancer 5 102–112 - PubMed
-
- Hecht, S. M. (2000) J. Nat. Prod. 63 158–168 - PubMed
-
- Boger, D. L., and Cai, H. (1999) Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38 448–476 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

