A synthetic mammalian electro-genetic transcription circuit
- PMID: 19190091
- PMCID: PMC2651811
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp014
A synthetic mammalian electro-genetic transcription circuit
Abstract
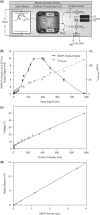
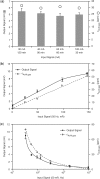
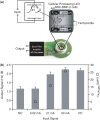
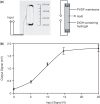
Electric signal processing has evolved to manage rapid information transfer in neuronal networks and muscular contraction in multicellular organisms and controls the most sophisticated man-built devices. Using a synthetic biology approach to assemble electronic parts with genetic control units engineered into mammalian cells, we designed an electric power-adjustable transcription control circuit able to integrate the intensity of a direct current over time, to translate the amplitude or frequency of an alternating current into an adjustable genetic readout or to modulate the beating frequency of primary heart cells. Successful miniaturization of the electro-genetic devices may pave the way for the design of novel hybrid electro-genetic implants assembled from electronic and genetic parts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Semi-synthetic mammalian gene regulatory networks.Metab Eng. 2005 Jul;7(4):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2005.02.005. Metab Eng. 2005. PMID: 16140238
-
6-hydroxy-nicotine-inducible multilevel transgene control in mammalian cells.Metab Eng. 2006 Nov;8(6):543-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2006.07.001. Epub 2006 Jul 22. Metab Eng. 2006. PMID: 16962351
-
Bile acid-controlled transgene expression in mammalian cells and mice.Metab Eng. 2014 Jan;21:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 24. Metab Eng. 2014. PMID: 24280297
-
Mammalian synthetic biology: engineering of sophisticated gene networks.J Biotechnol. 2007 Jul 15;130(4):329-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.05.014. Epub 2007 May 24. J Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17602777 Review.
-
Precision control of recombinant gene transcription for CHO cell synthetic biology.Biotechnol Adv. 2016 Sep-Oct;34(5):492-503. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.12.012. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Biotechnol Adv. 2016. PMID: 26721629 Review.
Cited by
-
Next-generation engineered microsystems for cell biology: a systems-level roadmap.Trends Cell Biol. 2022 Jun;32(6):490-500. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.01.003. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Trends Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35105487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electronic signals are electrogenetically relayed to control cell growth and co-culture composition.Metab Eng Commun. 2021 Jun 13;13:e00176. doi: 10.1016/j.mec.2021.e00176. eCollection 2021 Dec. Metab Eng Commun. 2021. PMID: 34194997 Free PMC article.
-
An electrogenetic interface to program mammalian gene expression by direct current.Nat Metab. 2023 Aug;5(8):1395-1407. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00850-7. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Nat Metab. 2023. PMID: 37524785 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic biology in the clinic: engineering vaccines, diagnostics, and therapeutics.Cell. 2021 Feb 18;184(4):881-898. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.017. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Cell. 2021. PMID: 33571426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electronic control of gene expression and cell behaviour in Escherichia coli through redox signalling.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 17;8:14030. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14030. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28094788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greber D, Fussenegger M. Mammalian synthetic biology: engineering of sophisticated gene networks. J. Biotechnol. 2007;130:329–345. - PubMed
-
- Deans TL, Cantor CR, Collins JJ. A tunable genetic switch based on RNAi and repressor proteins for regulating gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 2007;130:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Rinaudo K, Bleris L, Maddamsetti R, Subramanian S, Weiss R, Benenson Y. A universal RNAi-based logic evaluator that operates in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007;25:795–801. - PubMed

