A minimized rRNA-binding site for ribosomal protein S4 and its implications for 30S assembly
- PMID: 19190093
- PMCID: PMC2665224
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp036
A minimized rRNA-binding site for ribosomal protein S4 and its implications for 30S assembly
Abstract
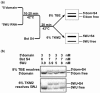
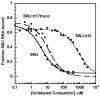
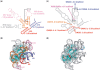
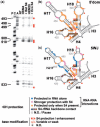
Primary ribosomal protein S4 is essential for 30S ribosome biogenesis in eubacteria, because it nucleates subunit assembly and helps coordinate assembly with the synthesis of its rRNA and protein components. S4 binds a five-helix junction (5WJ) that bridges the 5' and 3' ends of the 16S 5' domain. To delineate which nucleotides contribute to S4 recognition, sequential deletions of the 16S 5' domain were tested in competitive S4-binding assays based on electrophoretic mobility shifts. S4 binds the minimal 5WJ RNA containing just the five-helix junction as well or better than with affinity comparable to or better than the 5' domain or native 16S rRNA. Internal deletions and point mutations demonstrated that helices 3, 4, 16 and residues at the helix junctions are necessary for S4 binding, while the conserved helix 18 pseudoknot is dispensable. Hydroxyl radical footprinting and chemical base modification showed that S4 makes the same interactions with minimal rRNA substrates as with the native 16S rRNA, but the minimal substrates are more pre-organized for binding S4. Together, these results suggest that favorable interactions with S4 offset the energetic penalty for folding the 16S rRNA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Specific contacts between protein S4 and ribosomal RNA are required at multiple stages of ribosome assembly.RNA. 2013 Apr;19(4):574-85. doi: 10.1261/rna.037028.112. Epub 2013 Feb 21. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23431409 Free PMC article.
-
S16 throws a conformational switch during assembly of 30S 5' domain.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Apr;16(4):438-45. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1585. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19343072 Free PMC article.
-
Directed hydroxyl radical probing of 16S rRNA using Fe(II) tethered to ribosomal protein S4.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1113-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1113. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7862644 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-protein interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA.Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):783-90. doi: 10.1126/science.2658053. Science. 1989. PMID: 2658053 Review.
-
The 30S ribosomal P site: a function of 16S rRNA.FEBS Lett. 2005 Feb 7;579(4):855-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.11.026. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15680962 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Increases the Cooperativity of Ribonucleoprotein Assembly.Cell. 2019 Nov 27;179(6):1370-1381.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.007. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31761536 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of the five-way junction in the ribosomal small subunit using hybrid MD-Gō simulations.J Phys Chem B. 2012 Jun 14;116(23):6819-31. doi: 10.1021/jp212614b. Epub 2012 May 25. J Phys Chem B. 2012. PMID: 22458631 Free PMC article.
-
RbfA and IF3 couple ribosome biogenesis and translation initiation to increase stress tolerance.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 10;48(1):359-372. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1065. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31728529 Free PMC article.
-
Global stabilization of rRNA structure by ribosomal proteins S4, S17, and S20.J Mol Biol. 2009 Sep 25;392(3):666-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.032. Epub 2009 Jul 16. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19616559 Free PMC article.
-
Disassembly of unstable RNA structures by an E. coli DEAD-box chaperone accelerates ribosome assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkaf104. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf104. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39988318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olsson MO, Isaksson LA. Analysis of rpsD mutations in Escherichia coli. III. Effects of rpsD mutations on expression of some ribosomal protein genes. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1979;169:271–278. - PubMed
-
- Deckman IC, Draper DE. Specific interaction between ribosomal protein S4 and the alpha operon messenger RNA. Biochemistry. 1985;24:7860–7865. - PubMed
-
- Tang CK, Draper DE. Evidence for allosteric coupling between the ribosome and repressor binding sites of a translationally regulated mRNA. Biochemistry. 1990;29:4434–4439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

