Characterization of pullulanase (PUL)-deficient mutants of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and the function of PUL on starch biosynthesis in the developing rice endosperm
- PMID: 19190097
- PMCID: PMC2652056
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ern349
Characterization of pullulanase (PUL)-deficient mutants of rice (Oryza sativa L.) and the function of PUL on starch biosynthesis in the developing rice endosperm
Abstract
Rice (Oryza sativa) allelic sugary1 (sug1) mutants defective in isoamylase 1 (ISA1) accumulate varying levels of starch and phytoglycogen in their endosperm, and the activity of a pullulanase-type of a debranching enzyme (PUL) was found to correlate closely with the severity of the sug1 phenotype. Thus, three PUL-deficient mutants were generated to investigate the function of PUL in starch biosynthesis. The reduction of PUL activity had no pleiotropic effects on the other enzymes involved in starch biosynthesis. The short chains (DP < or = 13) of amylopectin in PUL mutants were increased compared with that of the wild type, but the extent of the changes was much smaller than that of sug1 mutants. The alpha-glucan composition [amylose, amylopectin, water-soluble polysaccharide (WSP)] and the structure of the starch components (amylose and amylopectin) of the PUL mutants were essentially the same, although the average chain length of the B(2-3) chains of amylopectin in the PUL mutant was approximately 3 residues longer than that of the wild type. The double mutants between the PUL-null and mild sug1 mutants still retained starch in the outer layer of endosperm tissue, while the amounts of WSP and short chains (DP < or = 7) of amylopectin were higher than those of the sug1 mutant; this indicates that the PUL function partially overlaps with that of ISA1 and its deficiency has a much smaller effect on the synthesis of amylopectin than ISA1 deficiency and the variation of the sug1 phenotype is not significantly dependent on the PUL activities.
Figures
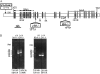


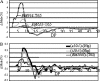


References
-
- Burton RA, Jenner H, Carrangis L, et al. Starch granule initiation and growth are altered in barley mutants that lack isoamylase activity. The Plant Journal. 2002;31:97–112. - PubMed
-
- Dauvillée D, Mestre V, Colleoni C, Slomianny MC, Mouille G, Delrue B, d'Hulst C, Bliard C, Nuzillard JM, Ball S. The debranching enzyme complex missing in glycogen accumulating mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii displays an isoamylase-type specificity. Plant Science. 2000;157:145–156. - PubMed
-
- Fox JD, Robyt JF. Miniaturization of three carbohydrate analyses using a microsample plate reader. Analytical Biochemistry. 1991;195:93–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

