CNOB/ChrR6, a new prodrug enzyme cancer chemotherapy
- PMID: 19190118
- PMCID: PMC2670992
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0707
CNOB/ChrR6, a new prodrug enzyme cancer chemotherapy
Abstract
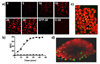
We report the discovery of a new prodrug, 6-chloro-9-nitro-5-oxo-5H-benzo(a)phenoxazine (CNOB). This prodrug is efficiently activated by ChrR6, the highly active prodrug activating bacterial enzyme we have previously developed. The CNOB/ChrR6 therapy was effective in killing several cancer cell lines in vitro. It also efficiently treated tumors in mice with up to 40% complete remission. 9-Amino-6-chloro-5H-benzo(a)phenoxazine-5-one (MCHB) was the only product of CNOB reduction by ChrR6. MCHB binds DNA; at nonlethal concentration, it causes cell accumulation in the S phase, and at lethal dose, it induces cell surface Annexin V and caspase-3 and caspase-9 activities. Further, MCHB colocalizes with mitochondria and disrupts their electrochemical potential. Thus, killing by CNOB involves MCHB, which likely induces apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. An attractive feature of the CNOB/ChrR6 regimen is that its toxic product, MCHB, is fluorescent. This feature proved helpful in in vitro studies because simple fluorescence measurements provided information on the kinetics of CNOB activation within the cells, MCHB killing mechanism, its generally efficient bystander effect in cells and cell spheroids, and its biodistribution. The emission wavelength of MCHB also permitted its visualization in live animals, allowing noninvasive qualitative imaging of MCHB in mice and the tumor microenvironment. This feature may simplify exploration of barriers to the penetration of MCHB in tumors and their amelioration.
Figures
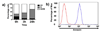




References
-
- Patterson AV, Saunders MP, Greco O. Prodrugs in genetic chemoradiotherapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:2131–2154. - PubMed
-
- Dachs GU, Tupper J, Tozer GM. From bench to bedside for gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy of cancer. Anti-cancer drugs. 2005;16:349–359. - PubMed
-
- Denny WA. Nitroreductase-based GDEPT. Curr Pharm Des. 2005:1349–1361. - PubMed
-
- Brown JM, Wilson WR. Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004;4:437–447. - PubMed
-
- Knox RJ, Chen S. Quinone reductase-mediated nitro-reduction: clinical applications. In: Sies H, Packer L, editors. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 382. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2004. pp. 194–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

