Melioidosis after brief exposure: a serologic survey in US Marines
- PMID: 19190209
- PMCID: PMC2774725
Melioidosis after brief exposure: a serologic survey in US Marines
Abstract
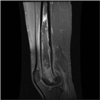
Melioidosis is endemic to Southeast Asia. The incidence of infection in visitors is not well known, especially for short visits. Thirteen (38%) of 34 previously unexposed US Marines had positive serology after 2 weeks in Thailand, and one developed acute disseminated disease. Asymptomatic infection with Burkholderia pseudomallei may be common, even from brief exposures.
Figures
Comment in
-
Positive serologic test results for Burkholderia pseudomallei in asymptomatic persons.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009 Jun;80(6):1065; author reply 1065-6. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009. PMID: 19478278 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yazdanpanah Y, Lemaire X, Senneville E, et al. Melioidotic Osteomyelitis of the Femur Occurring in a Traveler. J Travel Med. 2002;9:53–54. - PubMed
-
- Currie BJ, Fisher DA, Howard DM, et al. Endemic Melioidosis in Tropical Northern Australia: A 10-Year Prospective Study and Review of the Literature. CID. 2000;31:981–986. - PubMed
-
- Smith MD, Wuthiekanun V, Walsh AL, et al. Quantitative Recovery of Burkholderia pseudomallei from Soil in Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med. 1995;89:488–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical