Circulating tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-4 (TIMP-4) in systemic sclerosis patients with elevated pulmonary arterial pressure
- PMID: 19190762
- PMCID: PMC2630404
- DOI: 10.1155/2008/164134
Circulating tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-4 (TIMP-4) in systemic sclerosis patients with elevated pulmonary arterial pressure
Abstract
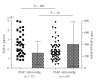
Decreased levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) or excess levels of their tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) may contribute to dysregulation of extracellular matrix turnover in systemic sclerosis (SSc). In a cross-sectional study of 106 SSc patients, we measured serum levels of TIMP-4 which is preferentially expressed in cardiovascular structures and searched for correlations with simultaneously performed echocardiography measurements of pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), myocardial performance, and pulmonary function tests. TIMP-4, but not MMP-9, levels were significantly raised in patients with SSc than controls. However, in the subgroup of patients with PASP measurements lower to 40 mmHg (n = 69), TIMP-4 levels were comparable to controls irrespective of the presence of diffuse or limited skin involvement, or lung fibrosis. Individual PASP measurements suggestive of pulmonary hypertension were associated with increased TIMP-4 serum levels (P = .03), independently of age, extent of skin sclerosis, or lung fibrosis, suggesting a cardiopulmonary vasculature-specific role of TIMP-4 activation in SSc.
Figures

References
-
- Denton CP, Black CM, Abraham DJ. Mechanisms and consequences of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology. 2006;2(3):134–144. - PubMed
-
- Charles C, Clements P, Furst DE. Systemic sclerosis: hypothesis-driven treatment strategies. The Lancet. 2006;367(9523):1683–1691. - PubMed
-
- Bull TM. Screening and therapy of pulmonary hypertension in systemic sclerosis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 2007;19(6):598–603. - PubMed
-
- Nagase H, Brew K. Designing TIMP (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases) variants that are selective metalloproteinase inhibitors. Biochemical Society Symposium. 2003;(70):201–212. - PubMed
-
- Koskivirta I, Rahkonen O, Mäyränpää M, et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 4 (TIMP4) is involved in inflammatory processes of human cardiovascular pathology. Histochemistry and Cell Biology. 2006;126(3):335–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

