Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce Th2-polarized immune response and promote endogenous repair in animal models of multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 19191336
- PMCID: PMC2706928
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.20841
Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce Th2-polarized immune response and promote endogenous repair in animal models of multiple sclerosis
Abstract
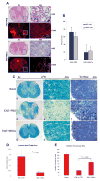
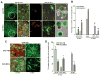
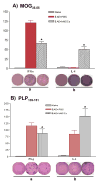
Cell-based therapies are attractive approaches to promote myelin repair. Recent studies demonstrated a reduction in disease burden in mice with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) treated with mouse mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Here, we demonstrated human bone marrow-derived MSCs (BM-hMSCs) promote functional recovery in both chronic and relapsing-remitting models of mouse EAE, traced their migration into the injured CNS and assayed their ability to modulate disease progression and the host immune response. Injected BM-hMSCs accumulated in the CNS, reduced the extent of damage and increased oligodendrocyte lineage cells in lesion areas. The increase in oligodendrocytes in lesions may reflect BM-hMSC-induced changes in neural fate determination, since neurospheres from treated animals gave rise to more oligodendrocytes and less astrocytes than nontreated neurospheres. Host immune responses were also influenced by BM-hMSCs. Inflammatory T-cells including interferon gamma producing Th1 cells and IL-17 producing Th17 inflammatory cells and their associated cytokines were reduced along with concomitant increases in IL-4 producing Th2 cells and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Together, these data suggest that the BM-hMSCs represent a viable option for therapeutic approaches.
Figures



References
-
- Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815–22. - PubMed
-
- Alexanian AR. Epigenetic modifiers promote efficient generation of neural-like cells from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells grown in neural environment. J Cell Biochem. 2007;100(2):362–71. - PubMed
-
- Ankeny DP, McTigue DM, Jakeman LB. Bone marrow tranplants provide tissue protectionadn directional guidance for axons after contusive spinal cord injuries in rats. Exp Neurology. 2004;190:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Antonysamy MA, Fanslow WC, Fu F, Li W, Qian S, Troutt AB, Thomson AW. Evidence for a role of IL-17 in alloimmunity: a novel IL-17 antagonist promotes heart graft survival. Transplant Proc. 1999;31(1-2):93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

