Role of high-affinity HLA-DP specific CLIP-derived peptides in beryllium binding to the HLA-DPGlu69 berylliosis-associated molecules and presentation to beryllium-sensitized T cells
- PMID: 19191908
- PMCID: PMC2753961
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03000.x
Role of high-affinity HLA-DP specific CLIP-derived peptides in beryllium binding to the HLA-DPGlu69 berylliosis-associated molecules and presentation to beryllium-sensitized T cells
Abstract
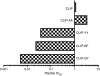
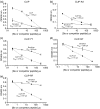
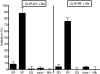
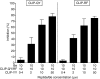
Berylliosis is driven by the accumulation in the lung of beryllium-specific T helper type 1 (Th1) cells recognizing beryllium as antigen when presented principally by human leucocyte antigen DP molecules carrying a glutamate at position beta69 (HLA-DPGlu69). This study was designed to clarify the precise role of peptides in beryllium binding to the HLA-DP groove's pocket 4 and to identify peptides with higher affinity for pocket 4 that might prevent beryllium presentation and T-cell stimulation. Beryllium/HLA-DP interactions were analysed by the ability of beryllium to compete with CLIP and CLIP-derived peptides to HLA-DPGlu69 soluble molecule. The CLIP-derived low-affinity peptide CLIP-AA, could not outcompete beryllium; while the CLIP-derived high-affinity peptides CLIP-YY, CLIP-QY and CLIP-RF were only marginally influenced by the presence of beryllium in the competition assay. The effect of these CLIP-derived high-affinity peptides on beryllium presentation was determined by measuring interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) release upon beryllium stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained from beryllium-hypersensitive subjects. CLIP-YY did inhibit beryllium presentation and T-cell activation, while CLIP-QY and CLIP-RF markedly enhanced the IFN-gamma response to beryllium. Anti-HLA-DP monoclonal antibody blocked the beryllium-induced IFN-gamma release in the presence of CLIP-QY (88%) and CLIP-RF (76%). A similar effect was observed for CLIP-YY capability to block IFN-gamma release by beryllium stimulation in the presence of CLIP-QY (79%) and CLIP-RF (76%). Overall, these data support the proposal that HLA-DP high-affinity peptides might be used as a model for specific berylliosis therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HLA-DP-unrestricted TNF-alpha release in beryllium-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Eur Respir J. 2002 Nov;20(5):1174-8. doi: 10.1183/09031936.02.02232001. Eur Respir J. 2002. PMID: 12449171
-
Beryllium binding to HLA-DP molecule carrying the marker of susceptibility to berylliosis glutamate beta 69.Hum Immunol. 2001 Jul;62(7):686-93. doi: 10.1016/s0198-8859(01)00261-0. Hum Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11423174
-
Role of the berylliosis-associated HLA-DPGlu69 supratypic variant in determining the response to beryllium in a blood T-cells beryllium-stimulated proliferation test.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2005 Oct;22(3):175-9. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2005. PMID: 16315779
-
Role of the HLA-DP Glu 69 and the TNF-alpha TNF-alpha 2 gene markers in susceptibility to beryllium hypersensitivity.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2004 May-Aug;17(2 Suppl):3-10. doi: 10.1177/03946320040170S202. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15345185 Review.
-
Chronic beryllium disease: T cell recognition of a metal presented by HLA-DP.Clin Immunol. 2001 Jul;100(1):4-14. doi: 10.1006/clim.2001.5053. Clin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11414740 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of HLA-DP2 and implications for chronic beryllium disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Apr 20;107(16):7425-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001772107. Epub 2010 Mar 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20356827 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide binding prediction for the human class II MHC allele HLA-DP2: a molecular docking approach.BMC Struct Biol. 2011 Jul 14;11:32. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-11-32. BMC Struct Biol. 2011. PMID: 21752305 Free PMC article.
-
Beryllium-Induced Hypersensitivity: Genetic Susceptibility and Neoantigen Generation.J Immunol. 2016 Jan 1;196(1):22-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502011. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26685315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide binding to HLA-DP proteins at pH 5.0 and pH 7.0: a quantitative molecular docking study.BMC Struct Biol. 2012 Aug 5;12:20. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-12-20. BMC Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22862845 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary granulomatosis of genetic origin.Eur Respir Rev. 2021 Apr 29;30(160):200152. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0152-2020. Print 2021 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. PMID: 33927005 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saltini C, Winestock K, Kirby M, Pinkston P, Crystal RG. Maintenance of alveolitis in patients with chronic beryllium disease by beryllium-specific helper T cells. N Engl J Med. 1989;320:1103–9. - PubMed
-
- Kreiss K, Miller F, Newman L, Ojo-Amaize EA, Rossman M, Saltini C. Chronic beryllium disease. From the workplace to cellular immunology, molecular immunogenetics, and back. Clin Immunol Immunopath. 1994;71:123–9. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, Sorrentino R, Saltini C. HLA-DPB1 glutamate 69: a genetic marker of beryllium disease. Science. 1993;262:242–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

