Interleukin-4 suppresses the cytotoxic potential of in vitro generated, adaptive regulatory CD4 T cells by down-regulation of granzyme B
- PMID: 19191911
- PMCID: PMC2712102
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02993.x
Interleukin-4 suppresses the cytotoxic potential of in vitro generated, adaptive regulatory CD4 T cells by down-regulation of granzyme B
Abstract
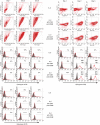
Regulatory CD4+ T cells (Tregs) control immune responses using secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines and/or cytotoxic mechanisms and play a central role in the outcomes of several immune pathologies. Previous studies suggest an impaired function of Tregs in allergy, especially during allergen seasons, but the underlying mechanism is not known. Therefore, we analysed the impact of the T helper type 2 cytokine interleukin (IL)-4 on in vitro generated adaptive Tregs (aTregs), which have been reported to use the granzyme B (GrB)/perforin pathway to kill autologous immune cells. aTregs were generated by co-ligation of CD3 and CD46 on CD4+ T lymphocytes and granzyme expression was analysed using flow cytometry. To quantify GrB and perforin expression as well as IL-10 secretion in response to IL-4, specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed in cell lysates and/or culture supernatants. Using a flow cytometry-based cytotoxicity assay the impact of IL-4 on the cytotoxic potential of aTregs was investigated. While IL-4 did not affect IL-10 secretion and perforin expression in aTregs, a significant suppression of GrB synthesis was detected in the presence of IL-4. In addition, IL-4-mediated suppression of GrB led to impaired cytotoxicity of aTregs against K562 target cells. In conclusion, our data suggest that IL-4 might play a role in impaired aTreg function in allergy.
Figures

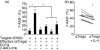
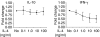
Similar articles
-
Reciprocal granzyme/perforin-mediated death of human regulatory and responder T cells is regulated by interleukin-2 (IL-2).J Mol Med (Berl). 2010 Jun;88(6):577-88. doi: 10.1007/s00109-010-0602-9. Epub 2010 Mar 12. J Mol Med (Berl). 2010. PMID: 20225066 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of granzyme B expression in T-cell receptor/CD28-stimulated human regulatory T cells is suppressed by inhibitors of the PI3K-mTOR pathway.BMC Immunol. 2009 Nov 22;10:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-10-59. BMC Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19930596 Free PMC article.
-
Functional expression of granzyme B in human plasmacytoid dendritic cells: a role in allergic inflammation.Clin Exp Allergy. 2010 Jul;40(7):1015-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03499.x. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010. PMID: 20412137
-
Induction of granzyme B and T cell cytotoxic capacity by IL-2 or IL-15 without antigens: multiclonal responses that are extremely lytic if triggered and short-lived after cytokine withdrawal.Cytokine. 2006 Nov;36(3-4):148-59. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2006.11.008. Epub 2006 Dec 22. Cytokine. 2006. PMID: 17188506 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell stimulation and regulation: with complements from CD46.Immunol Res. 2005;32(1-3):31-43. doi: 10.1385/IR:32:1-3:031. Immunol Res. 2005. PMID: 16106057 Review.
Cited by
-
Heligmosomoides bakeri and Toxoplasma gondii co-infection leads to increased mortality associated with changes in immune resistance in the lymphoid compartment and disease pathology.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 1;19(7):e0292408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292408. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38950025 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical development and molecular characterization of an engineered type 1 regulatory T-cell product suitable for immunotherapy.Cytotherapy. 2021 Nov;23(11):1017-1028. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2021.05.010. Epub 2021 Aug 15. Cytotherapy. 2021. PMID: 34404616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–6. - PubMed
-
- Stock P, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Inhibition of the allergic response by regulatory T cells. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;6:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Hawrylowicz CM, O’Garra A. Potential role of interleukin-10-secreting regulatory T cells in allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:271–83. - PubMed
-
- Kemper C, Chan AC, Green JM, Brett KA, Murphy KM, Atkinson JP. Activation of human CD4+ cells with CD3 and CD46 induces a T-regulatory cell 1 phenotype. Nature. 2003;421:388–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

