Interleukin-4 suppresses the cytotoxic potential of in vitro generated, adaptive regulatory CD4 T cells by down-regulation of granzyme B
- PMID: 19191911
- PMCID: PMC2712102
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02993.x
Interleukin-4 suppresses the cytotoxic potential of in vitro generated, adaptive regulatory CD4 T cells by down-regulation of granzyme B
Abstract
Regulatory CD4+ T cells (Tregs) control immune responses using secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines and/or cytotoxic mechanisms and play a central role in the outcomes of several immune pathologies. Previous studies suggest an impaired function of Tregs in allergy, especially during allergen seasons, but the underlying mechanism is not known. Therefore, we analysed the impact of the T helper type 2 cytokine interleukin (IL)-4 on in vitro generated adaptive Tregs (aTregs), which have been reported to use the granzyme B (GrB)/perforin pathway to kill autologous immune cells. aTregs were generated by co-ligation of CD3 and CD46 on CD4+ T lymphocytes and granzyme expression was analysed using flow cytometry. To quantify GrB and perforin expression as well as IL-10 secretion in response to IL-4, specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed in cell lysates and/or culture supernatants. Using a flow cytometry-based cytotoxicity assay the impact of IL-4 on the cytotoxic potential of aTregs was investigated. While IL-4 did not affect IL-10 secretion and perforin expression in aTregs, a significant suppression of GrB synthesis was detected in the presence of IL-4. In addition, IL-4-mediated suppression of GrB led to impaired cytotoxicity of aTregs against K562 target cells. In conclusion, our data suggest that IL-4 might play a role in impaired aTreg function in allergy.
Figures

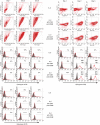
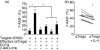
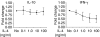
References
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–6. - PubMed
-
- Stock P, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. Inhibition of the allergic response by regulatory T cells. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;6:12–16. - PubMed
-
- Hawrylowicz CM, O’Garra A. Potential role of interleukin-10-secreting regulatory T cells in allergy and asthma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:271–83. - PubMed
-
- Kemper C, Chan AC, Green JM, Brett KA, Murphy KM, Atkinson JP. Activation of human CD4+ cells with CD3 and CD46 induces a T-regulatory cell 1 phenotype. Nature. 2003;421:388–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

