Characteristics of bortezomib- and thalidomide-induced peripheral neuropathy
- PMID: 19192067
- PMCID: PMC3741683
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1529-8027.2008.00193.x
Characteristics of bortezomib- and thalidomide-induced peripheral neuropathy
Abstract
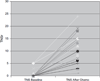
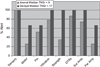
Dose-limiting peripheral neuropathy (PN) is frequently reported with the use of thalidomide and bortezomib, novel proteasome inhibitors. While these two agents have significant activity in multiple myeloma (MM), the combination and the associated PN have not been fully examined in untreated patients. The objective of this study was to report the baseline prevalence and occurrence of PN in newly diagnosed MM patients treated with bortezomib and thalidomide. Twenty-seven patients (11 men and 16 women) with previously untreated MM were prospectively monitored for PN. Total neuropathy score reduced (TNSr) was calculated at baseline and after every two cycles of bortezomib treatment. The median cumulative dose of bortezomib was 35.6 mg/m(2) (median 8 cycles) and of thalidomide was 16.8 g. Only three subjects showed mild PN at baseline (whole group median TNSr 0). At the end of treatment, PN developed in 26 patients (median TNSr 8). PN was of mild to moderate severity (TNSr grade 1 = 11, grade 2 = 10, grade 3 = 5, and grade 4 = 0). Nerve conduction studies showed axonal physiology in all except three subjects in whom demyelinating physiology was noted. The median TNSr was 17 in the demyelinating group and 9 in the axonal group. There was no significant correlation of TNSr with cumulative bortezomib or thalidomide dose. At follow-up, 80% of patients had become asymptomatic after discontinuation of the chemotherapy. We conclude that bortezomib and thalidomide combination chemotherapy induces a reversible length-dependent sensory>motor, predominantly axonal, large-fiber>small-fiber polyneuropathy. In a subset, a more severe demyelinating polyneuropathy may develop.
Figures
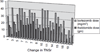

References
-
- Badros A, Goloubeva O, Dalal JS, Can I, Thompson J, Rapoport AP, Heyman M, Akpek G, Fenton RG. Neurotoxicity of bortezomib therapy in multiple myeloma: a single-center experience and review of the literature. Cancer. 2007;110:1042–1049. - PubMed
-
- Bang SM, Lee JH, Yoon SS, Park S, Min CK, Kim CC, Suh C, Sohn SK, Min YH, Lee JJ, Kim K, Seong CM, Yoon HJ, Cho KS, Jo DY, Lee KH, Lee NR, Kim CS. A multicenter retrospective analysis of adverse events in Korean patients using bortezomib for multiple myeloma. Int J Hematol. 2006;83:309–313. - PubMed
-
- Barlogie B, Tricot G, Anaissie E. Thalidomide in the management of multiple myeloma. Semin Oncol. 2001;28:577–582. - PubMed
-
- Cavaletti G, Beronio A, Reni L, Ghiglione E, Schenone A, Briani C, Zara G, Cocito D, Isoardo G, Ciaramitaro P, Plasmati R, Pastorelli F, Frigo M, Piatti M, Carpo M. Thalidomide sensory neurotoxicity: a clinical and neurophysiologic study. Neurology. 2004;62:2291–2293. - PubMed
-
- Cavaletti G, Jann S, Pace A, Plasmati R, Siciliano G, Briani C, Cocito D, Padua L, Ghiglione E, Manicone M, Giussani G. Multi-center assessment of the Total Neuropathy Score for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2006;11:135–141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

