Autoantibodies to heat shock protein 60 promote thrombus formation in a murine model of arterial thrombosis
- PMID: 19192108
- PMCID: PMC3429411
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03305.x
Autoantibodies to heat shock protein 60 promote thrombus formation in a murine model of arterial thrombosis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Anti-heat shock protein (HSP)60 autoantibodies are associated with atherosclerosis and are known to affect endothelial cells in vitro. However, their role in thrombus formation remains unclear. We hypothesized that anti-HSP60 autoantibodies could potentiate thrombosis, and evaluated the effect of anti-murine HSP60 antibodies in a ferric chloride (FeCl3)-induced murine model of carotid artery injury.
Methods: Anti-HSP60, or control, IgG was administered to BALB/c mice 48 h prior to inducing carotid artery injury, and blood flow was monitored using an ultrasound probe.
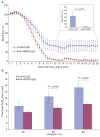
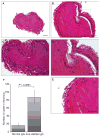
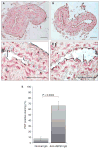
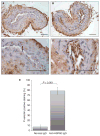
Results: Thrombus formation was more rapid and stable in anti-HSP60 IGG-treated mice than in controls (blood flow=1.7%+/-0.6% vs. 34%+/-12.6%, P=0.0157). Occlusion was complete in all anti-HSP60 IgG-treated mice (13/13), with no reperfusion being observed. In contrast, 64% (9/14) of control mice had complete occlusion, with reperfusion occurring in 6/9 mice. Thrombi were significantly larger in anti-HSP60 IgG-treated mice (P=0.0001), and contained four-fold more inflammatory cells (P=0.0281) than in controls. Non-injured contralateral arteries of anti-HSP60 IgG-treated mice were also affected, exhibiting abnormal endothelial cell morphology and significantly greater von Willebrand factor (VWF) and P-selectin expression than control mice (P=0.0024 and P=0.001, respectively).
Conclusions: In summary, the presence of circulating anti-HSP60 autoantibodies resulted in increased P-selectin and VWF expression and altered cell morphology in endothelial cells lining uninjured carotid arteries, and promoted thrombosis and inflammatory cell recruitment in FeCl3-injured carotid arteries. These findings suggest that anti-HSP60 autoantibodies may constitute an important prothrombotic risk factor in cardiovascular disease in human vascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
M. A. Gillis, J. F. Théorêt and G. Lajoie state that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
P-selectin can promote thrombus propagation independently of both von Willebrand factor and thrombospondin-1 in mice.J Thromb Haemost. 2017 Feb;15(2):388-394. doi: 10.1111/jth.13586. Epub 2017 Feb 3. J Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 27943541 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies against heat shock protein 60 mediate endothelial cytotoxicity.J Clin Invest. 1995 Dec;96(6):2569-77. doi: 10.1172/JCI118320. J Clin Invest. 1995. PMID: 8675620 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cell-Derived von Willebrand Factor Is the Major Determinant That Mediates von Willebrand Factor-Dependent Acute Ischemic Stroke by Promoting Postischemic Thrombo-Inflammation.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Sep;36(9):1829-37. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.307660. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 27444201 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of endothelial cell damages by anti-Hsp60 autoantibodies in systemic autoimmune diseases.Autoimmun Rev. 2007 Aug;6(7):438-43. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2007.01.012. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Autoimmun Rev. 2007. PMID: 17643930 Review.
-
HSP60 and anti-HSP60 antibodies in vasculitis: they are two of a kind.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008 Oct;35(1-2):66-71. doi: 10.1007/s12016-007-8062-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18188708 Review.
Cited by
-
"Gum bug, leave my heart alone!"--epidemiologic and mechanistic evidence linking periodontal infections and atherosclerosis.J Dent Res. 2010 Sep;89(9):879-902. doi: 10.1177/0022034510375281. Epub 2010 Jul 16. J Dent Res. 2010. PMID: 20639510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of seropositivity to Chlamydia pneumoniae and anti-hHSP60 on cardiovascular events in hemodialysis patients.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011 Mar;16(2):219-24. doi: 10.1007/s12192-010-0235-5. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2011. PMID: 20922511 Free PMC article.
-
Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydial Heat Shock Protein 60 and Anti-Chlamydial Antibodies in Women with Epithelial Ovarian Tumors.Transl Oncol. 2018 Apr;11(2):546-551. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.02.008. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29524832 Free PMC article.
-
Auto-antibodies as emergent prognostic markers and possible mediators of ischemic cardiovascular diseases.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013 Feb;44(1):84-97. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8233-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013. PMID: 21188647 Review.
-
Relationship between intrathrombotic appearance of HSP27 and HSP70 and thrombus ages in a murine model of deep vein thrombosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 16;13(1):22416. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48987-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38104135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wick G, Knoflach M, Xu Q. Autoimmune and inflammatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:361–403. - PubMed
-
- Mayr M, Kiechl S, Willeit J, Wick G, Xu Q. Infections, immunity, and atherosclerosis: associations of antibodies to Chlamydia pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori, and cytomegalovirus with immune reactions to heat-shock protein 60 and carotid or femoral atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2000;102:833–9. - PubMed
-
- Xu Q, Schett G, Seitz CS, Hu Y, Gupta RS, Wick G. Surface staining and cytotoxic activity of heat-shock protein 60 antibody in stressed aortic endothelial cells. Circ Res. 1994;75:1078–85. - PubMed
-
- Pfister G, Stroh CM, Perschinka H, Kind M, Knoflach M, Hinterdorfer P, Wick G. Detection of HSP60 on the membrane surface of stressed human endothelial cells by atomic force and confocal microscopy. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:1587–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

