alpha-Synuclein and neuronal cell death
- PMID: 19193223
- PMCID: PMC2646729
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-9
alpha-Synuclein and neuronal cell death
Abstract
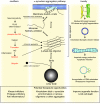
alpha-Synuclein is a small protein that has special relevance for understanding Parkinson disease and related disorders. Not only is alpha-synuclein found in Lewy bodies characteristic of Parkinson disease, but also mutations in the gene for alpha-synuclein can cause an inherited form of Parkinson disease and expression of normal alpha-synuclein can increase the risk of developing Parkinson disease in sporadic, or non-familial, cases. Both sporadic and familial Parkinson disease are characterized by substantial loss of several groups of neurons, including the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra that are the target of most current symptomatic therapies. Therefore, it is predicted that alpha-synuclein, especially in its mutant forms or under conditions where its expression levels are increased, is a toxic protein in the sense that it is associated with an increased rate of neuronal cell death. This review will discuss the experimental contexts in which alpha-synuclein has been demonstrated to be toxic. I will also outline what is known about the mechanisms by which alpha-synuclein triggers neuronal damage, and identify some of the current gaps in our knowledge about this subject. Finally, the therapeutic implications of toxicity of alpha-synuclein will be discussed.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

