Melatonin and breast cancer: cellular mechanisms, clinical studies and future perspectives
- PMID: 19193248
- PMCID: PMC4301735
- DOI: 10.1017/S1462399409000982
Melatonin and breast cancer: cellular mechanisms, clinical studies and future perspectives
Abstract
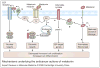
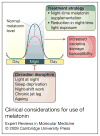
Recent studies have suggested that the pineal hormone melatonin may protect against breast cancer, and the mechanisms underlying its actions are becoming clearer. Melatonin works through receptors and distinct second messenger pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and to induce cellular differentiation. In addition, independently of receptors melatonin can modulate oestrogen-dependent pathways and reduce free-radical formation, thus preventing mutation and cellular toxicity. The fact that melatonin works through a myriad of signalling cascades that are protective to cells makes this hormone a good candidate for use in the clinic for the prevention and/or treatment of cancer. This review summarises cellular mechanisms governing the action of melatonin and then considers the potential use of melatonin in breast cancer prevention and treatment, with an emphasis on improving clinical outcomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Melatonin, experimental basis for a possible application in breast cancer prevention and treatment.Histol Histopathol. 2000 Apr;15(2):637-47. doi: 10.14670/HH-15.637. Histol Histopathol. 2000. PMID: 10809385 Review.
-
Melatonin: A Potential Antineoplastic Agent in Breast Cancer.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2022;41(4):55-84. doi: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2022041294. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36374962 Review.
-
Melatonin synergizes with retinoic acid in the prevention and regression of breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;460:345-62. doi: 10.1007/0-306-46814-x_39. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10810532 Review. No abstract available.
-
Melatonin and cancer: From the promotion of genomic stability to use in cancer treatment.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5613-5627. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27391. Epub 2018 Sep 21. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30238978 Review.
-
Melatonin and mammary pathological growth.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2000 Apr;21(2):133-70. doi: 10.1006/frne.1999.0194. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10764528 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Melatonin, Estrogen, and Progesterone Hormone Therapy Demonstrates Anti-Cancer Actions in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2020 Jun 24;14:1178223420924634. doi: 10.1177/1178223420924634. eCollection 2020. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2020. PMID: 32636633 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin and Cancer: A Polyhedral Network Where the Source Matters.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 1;10(2):210. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020210. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33535472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic and epigenetic alterations in night shift nurses with breast cancer: a narrative review.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jan 20;25(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12935-025-03649-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 39833897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on the role of melatonin in the prevention of cancer tumorigenesis and in the management of cancer correlates, such as sleep-wake and mood disturbances: review and remarks.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013 Oct;25(5):499-510. doi: 10.1007/s40520-013-0118-6. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 24046037 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial functions and melatonin: a tour of the reproductive cancers.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Mar;76(5):837-863. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2963-0. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30430198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reiter RJ. Pineal melatonin: cell biology of its synthesis and of its physiological interactions. Endocrine Reviews. 1991;12:151–180. - PubMed
-
- Pandi-Perumal SR, et al. Role of the melatonin system in the control of sleep: therapeutic implications. CNS Drugs. 2007;21:995–1018. - PubMed
-
- Witt-Enderby PA, et al. Melatonin receptors and their regulation: biochemical and structural mechanisms. Life Sciences. 2003;72:2183–2198. - PubMed
-
- Poirel VJ, et al. MT1 melatonin receptor mRNA expression exhibits a circadian variation in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei. Brain Research. 2002;946:64–71. - PubMed
-
- Gauer F, et al. Daily rhythms of melatonin binding sites in the rat pars tuberalis and suprachiasmatic nuclei; evidence for a regulation of melatonin receptors by melatonin itself. Neuroendocrinology. 1993;57:120–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

