Severe dengue epidemics in Sri Lanka, 2003-2006
- PMID: 19193262
- PMCID: PMC2662655
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1502.080926
Severe dengue epidemics in Sri Lanka, 2003-2006
Abstract
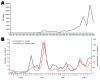
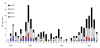
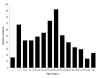
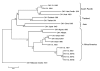
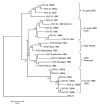
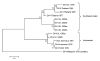
Recent emergence of dengue hemorrhagic fever in the Indian subcontinent has been well documented in Sri Lanka. We compare recent (2003-2006) and past (1980-1997) dengue surveillance data for Sri Lanka. The 4 dengue virus (DENV) serotypes have been cocirculating in Sri Lanka for >30 years. Over this period, a new genotype of DENV-1 has replaced an old genotype. Moreover, new clades of DENV-3 genotype III viruses have replaced older clades. Emergence of new clades of DENV-3 in 1989 and 2000 coincided with abrupt increases in the number of reported dengue cases, implicating this serotype in severe epidemics. In 1980-1997, most reported dengue cases were in children. Recent epidemics have been characterized by many cases in children and adults. Changes in local transmission dynamics and genetic changes in DENV-3 are likely increasing emergence of severe dengue epidemics in Sri Lanka.
Figures

References
-
- Innis BL. Antibody responses to dengue virus infection. In: Gubler DJ, Kuno G, editors. Dengue and dengue hemorrhagic fever. New York: CAB International; 1997. p. 221–44.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
