Deficiency in Six2 during prenatal development is associated with reduced nephron number, chronic renal failure, and hypertension in Br/+ adult mice
- PMID: 19193724
- PMCID: PMC2681363
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.90550.2008
Deficiency in Six2 during prenatal development is associated with reduced nephron number, chronic renal failure, and hypertension in Br/+ adult mice
Abstract
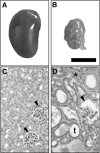
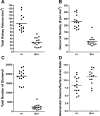
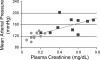
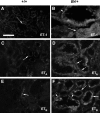
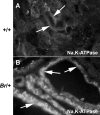
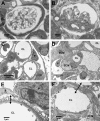
The Br/+ mutant mouse displays decreased embryological expression of the homeobox transcription factor Six2, resulting in hertitable renal hypoplasia. The purpose of this study was to characterize the renal physiological consequences of embryonic haploinsuffiency of Six2 by analyzing renal morphology and function in the adult Br heterozygous mutant. Adult Br/+ kidneys weighed 50% less than those from wild-type mice and displayed glomerulopathy. Stereological analysis of renal glomeruli showed that Br/+ kidneys had an average of 88% fewer glomeruli than +/+ kidneys, whereas individual glomeruli in Br/+ mice maintained an average volume increase of 180% compared with normal nephrons. Immunostaining revealed increased levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1), endothelin receptors A (ET(A)) and B (ET(B)), and Na-K-ATPase were present in the dilated renal tubules of mutant mice. Physiological features of chronic renal failure (CRF) including elevated mean arterial pressure, increased plasma creatinine, and dilute urine excretion were measured in Br/+ mutant mice. Electron microscopy of the Br/+ glomeruli revealed pathological alterations such as hypercellularity, extracellular matrix accumulation, and a thick irregular glomerular basement membrane. These results indicate that adult Br/+ mice suffer from CRF associated with reduced nephron number and renal hypoplasia, as well as glomerulopathy. Defects are associated with embryological deficiencies of Six2, suggesting that proper levels of this protein during nephrogenesis are critical for normal glomerular development and adult renal function.
Figures
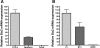
Similar articles
-
Osmoregulatory defect in adult mice associated with deficient prenatal expression of six2.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):R682-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00187.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21653879 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulatory control of mammalian nephron progenitors revealed by multi-factor cistromic analysis and genetic studies.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jan 29;14(1):e1007181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007181. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29377931 Free PMC article.
-
Misexpression of Six2 is associated with heritable frontonasal dysplasia and renal hypoplasia in 3H1 Br mice.Dev Dyn. 2008 Jul;237(7):1767-79. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21587. Dev Dyn. 2008. PMID: 18570229 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital oligonephropathy and the etiology of adult hypertension and progressive renal injury.Am J Kidney Dis. 1994 Feb;23(2):171-5. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994. PMID: 8311070 Review.
-
Kidney morphology: update 1985.Toxicol Pathol. 1986;14(1):13-25. doi: 10.1177/019262338601400103. Toxicol Pathol. 1986. PMID: 3520780 Review.
Cited by
-
PRISM offers a comprehensive genomic approach to transcription factor function prediction.Genome Res. 2013 May;23(5):889-904. doi: 10.1101/gr.139071.112. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23382538 Free PMC article.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System in the Development of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in Animal Models and Humans.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010 Mar 29;3(4):940-960. doi: 10.3390/ph3040940. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2010. PMID: 27713283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of gestational low-protein intake on embryonic kidney microRNA expression and in nephron progenitor cells of the male fetus.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 5;16(2):e0246289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246289. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33544723 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroproliferative response to urothelial failure obliterates the ureter lumen in a mouse model of prenatal congenital obstructive nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 11;6:31137. doi: 10.1038/srep31137. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27511831 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental expression patterns of candidate cofactors for vertebrate six family transcription factors.Dev Dyn. 2010 Dec;239(12):3446-66. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22484. Dev Dyn. 2010. PMID: 21089078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis 39: S1–S266, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Alarcon VB, Marikawa Y. Molecular study of mouse peri-implantation development using the in vitro culture of aggregated inner cell mass. Mol Reprod Dev 67: 83–90, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Andreoli SP Acute renal failure in the newborn. Semin Perinatol 28: 112–123, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Avner ED Epithelial polarity and differentiation in polycystic kidney disease. J Cell Sci Suppl 17: 217–222, 1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

