1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses high glucose-induced angiotensinogen expression in kidney cells by blocking the NF-{kappa}B pathway
- PMID: 19193728
- PMCID: PMC2681355
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00002.2009
1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses high glucose-induced angiotensinogen expression in kidney cells by blocking the NF-{kappa}B pathway
Abstract
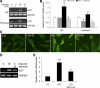
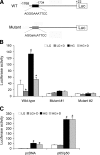
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is a major mediator of renal injury in diabetic nephropathy. Our previous studies demonstrated that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,25(OH)(2)D(3)] plays a renoprotective role by suppressing the RAS, with renin and angiotensinogen (AGT) as the main targets. The mechanism whereby 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) transcriptionally suppresses renin gene expression has been elucidated; however, how vitamin D regulates AGT remains unknown. Exposure of mesangial cells or podocytes to high glucose (HG; 30 mM) markedly stimulated AGT expression. In mesangial cells, the stimulation was inhibited by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) (20 nM) or NF-kappaB inhibitor BAY 11-7082, suggesting the involvement of NF- kappaB in HG-induced AGT expression and the interaction between 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) and NF-kappaB in the regulation. Plasmid pNF-kappaB-Luc luciferase reporter assays showed that 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) blocked HG-induced NF-kappaB activity. EMSA and ChIP assays demonstrated increased p65/p50 binding to a NF-kappaB binding site at -1734 in the AGT gene promoter upon high glucose stimulation, and the binding was disrupted by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) treatment. Overexpression of p65/p50 overcame 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) suppression, and mutation of this NF-kappaB binding site blunted 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) suppression of the promoter activity. In mice lacking the vitamin D receptor, AGT mRNA expression in the kidney was markedly increased compared with wild-type mice, and AGT induction in diabetic mice was suppressed by treatment with a vitamin D analog. These data indicate that 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) suppresses hyperglycemia-induced AGT expression by blocking NF-kappaB-mediated pathway.
Figures
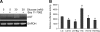

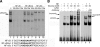
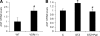
References
-
- Anderson S, Jung FF, Ingelfinger JR. Renal renin-angiotensin system in diabetes: functional, immunohistochemical, and molecular biological correlations. Am J Physiol Renal Fluid Electrolyte Physiol 265: F477–F486, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Carey RM, Siragy HM. The intrarenal renin-angiotensin system and diabetic nephropathy. Trends Endocrinol Metab 14: 274–281, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Dong X, Craig T, Xing N, Bachman LA, Paya CV, Weih F, McKean DJ, Kumar R, Griffin MD. Direct transcriptional regulation of RelB by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs: physiologic and therapeutic implications for dendritic cell function. J Biol Chem 278: 49378–49385, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Durvasula RV, Shankland SJ. Activation of a local renin angiotensin system in podocytes by glucose. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294: F830–F839, 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

