In vivo gp41 antibodies targeting the 2F5 monoclonal antibody epitope mediate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization breadth
- PMID: 19193787
- PMCID: PMC2663270
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02631-08
In vivo gp41 antibodies targeting the 2F5 monoclonal antibody epitope mediate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization breadth
Abstract
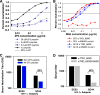
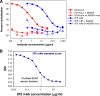
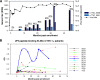
The broadly neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) 2F5 and 4E10, both targeting the highly conserved human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope membrane proximal external region (MPER), are among the MAbs with the broadest heterologous neutralizing activity and are of considerable interest for HIV-1 vaccine development. We have identified serum antibodies from an HIV-infected subject that both were broadly neutralizing and specifically targeted MPER epitopes that overlap the 2F5 epitope. These MPER-specific antibodies were made 15 to 20 months following transmission and concomitantly with the development of autoantibodies. Our findings suggest that multiple events (i.e., genetic predisposition and HIV-1 immune dysregulation) may be required for induction of broadly reactive gp41 MPER antibodies in natural infection.
Figures





References
-
- Alam, S. M., R. M. Scearce, R. J. Parks, K. Plonk, S. G. Plonk, L. L. Sutherland, M. K. Gorny, S. Zolla-Pazner, S. Vanleeuwen, M. A. Moody, S. M. Xia, D. C. Montefiori, G. D. Tomaras, K. J. Weinhold, S. A. Karim, C. B. Hicks, H. X. Liao, J. Robinson, G. M. Shaw, and B. F. Haynes. 2008. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 antibodies that mask membrane proximal region epitopes: antibody binding kinetics, induction, and potential for regulation in acute infection. J. Virol. 82115-125. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binley, J. M., E. A. Lybarger, E. T. Crooks, M. S. Seaman, E. Gray, K. L. Davis, J. M. Decker, D. Wycuff, L. Harris, N. Hawkins, B. Wood, C. Nathe, D. Richman, G. D. Tomaras, F. Bibollet-Ruche, J. E. Robinson, L. Morris, G. M. Shaw, D. C. Montefiori, and J. R. Mascola. 2008. Profiling the specificity of neutralizing antibodies in a large panel of plasmas from patients chronically infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtypes B and C. J. Virol. 8211651-11668. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blattner, W. A., K. A. Oursler, F. Cleghorn, M. Charurat, A. Sill, C. Bartholomew, N. Jack, T. O'Brien, J. Edwards, G. Tomaras, K. Weinhold, and M. Greenberg. 2004. Rapid clearance of virus after acute HIV-1 infection: correlates of risk of AIDS. J. Infect. Dis. 1891793-1801. - PubMed
-
- Buchacher, A., R. Predl, K. Strutzenberger, W. Steinfellner, A. Trkola, M. Purtscher, G. Gruber, C. Tauer, F. Steindl, A. Jungbauer, et al.1994. Generation of human monoclonal antibodies against HIV-1 proteins; electrofusion and Epstein-Barr virus transformation for peripheral blood lymphocyte immortalization. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 10359-369. - PubMed
-
- Chen, W., Z. Zhu, M. Zhang, A. Macagno, P. Prabakaran, J. Owens, N. S. Longo, M. Markowitz, A. Lanzavecchia, B. F. Haynes, and D. S. Dimitrov. 2008. All known cross reactive HIV-1 neutralizing antibodies are highly divergent from germline and their elicitation may require prolonged periods of time, abstr. OA03-03. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 24(Suppl. 1)11-12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

