Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus S-segment untranslated regions mediate poly(A) tail-independent translation
- PMID: 19193790
- PMCID: PMC2663239
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02201-08
Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus S-segment untranslated regions mediate poly(A) tail-independent translation
Abstract
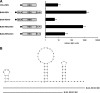
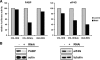
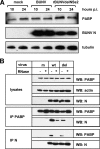
The mRNAs of Bunyamwera virus (BUNV), the prototype of the Bunyaviridae family, possess a 5' cap structure but lack a 3' poly(A) tail, a common feature of eukaryotic mRNAs that greatly enhances translation efficiency. Viral mRNAs also contain untranslated regions (UTRs) that flank the coding sequence. Using model virus-like mRNAs that harbor the Renilla luciferase reporter gene, we found that the 3' UTR of the BUNV small-segment mRNA mediated efficient translation in the absence of a poly(A) tail. Viral UTRs did not increase RNA stability, and polyadenylation did not significantly enhance reporter activity. Translation of virus-like mRNAs in transfected cells was unaffected by knockdown of poly(A)-binding protein (PABP) but was markedly reduced by depletion of eukaryotic initiation factor 4G, suggesting a PABP-independent process for translation initiation. In BUNV-infected cells, translation of polyadenylated but not virus-like mRNAs was inhibited. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the viral nucleocapsid protein binds to, and colocalizes with, PABP in the cytoplasm early in infection, followed by nuclear retention of PABP. Our results suggest that BUNV corrupts PABP function in order to inhibit translation of polyadenylated cellular mRNAs while its own mRNAs are translated in a PABP-independent process.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Poly(A)-binding protein facilitates translation of an uncapped/nonpolyadenylated viral RNA by binding to the 3' untranslated region.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(15):7836-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00538-12. Epub 2012 May 16. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22593149 Free PMC article.
-
Viral and cellular mRNA-specific activators harness PABP and eIF4G to promote translation initiation downstream of cap binding.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 13;114(24):6310-6315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610417114. Epub 2017 May 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28559344 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4G-poly(A) binding protein interaction is required for poly(A) tail-mediated stimulation of picornavirus internal ribosome entry segment-driven translation but not for X-mediated stimulation of hepatitis C virus translation.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jul;21(13):4097-109. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.13.4097-4109.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11390639 Free PMC article.
-
Translational control of mRNAs by 3'-Untranslated region binding proteins.BMB Rep. 2017 Apr;50(4):194-200. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2017.50.4.040. BMB Rep. 2017. PMID: 28287067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of poly(A)-binding protein through PABP-interacting proteins.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:537-43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.061. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381337 Review.
Cited by
-
The mammalian orthoreovirus bicistronic M3 mRNA initiates translation using a 5' end-dependent, scanning mechanism that does not require interaction of 5'-3' untranslated regions.Virus Res. 2014 Apr;183:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.01.018. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24486484 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of tripartite RNA genome packaging in Rift Valley fever virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 11;108(2):804-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013155108. Epub 2010 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21187405 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping overlapping functional elements embedded within the protein-coding regions of RNA viruses.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Nov 10;42(20):12425-39. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku981. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 25326325 Free PMC article.
-
Tick-borne encephalitis virus inhibits rRNA synthesis and host protein production in human cells of neural origin.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Sep 27;13(9):e0007745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007745. eCollection 2019 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31560682 Free PMC article.
-
Uukuniemi virus infection causes a pervasive remodelling of the RNA-binding proteome in tick cells.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Aug 4;21(8):e1013393. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013393. eCollection 2025 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40758761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afonina, E., R. Stauber, and G. N. Pavlakis. 1998. The human poly(A)-binding protein 1 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 27313015-13021. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. S. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1992. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Boston, MA.
-
- Barr, J. N., J. W. Rodgers, and G. W. Wertz. 2006. Identification of the Bunyamwera bunyavirus transcription termination signal. J. Gen. Virol. 87189-198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

