The replication cycle of varicella-zoster virus: analysis of the kinetics of viral protein expression, genome synthesis, and virion assembly at the single-cell level
- PMID: 19193797
- PMCID: PMC2663235
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02137-08
The replication cycle of varicella-zoster virus: analysis of the kinetics of viral protein expression, genome synthesis, and virion assembly at the single-cell level
Abstract
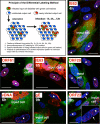
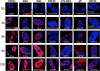
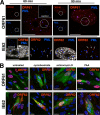
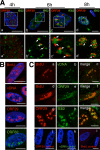
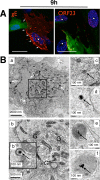
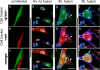
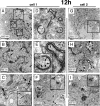
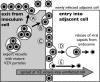
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a human alphaherpesvirus that is highly cell associated in cell culture. Because cell-free virus yields are too low to permit the synchronous infections needed for time-resolved analyses, information is lacking about the sequence of events during the VZV replication cycle. To address this challenge, we differentially labeled VZV-infected inoculum cells (input) and uninfected (output) cells with fluorescent cell dyes or endocytosed nanogold particles and evaluated newly infected cells by confocal immunofluorescence or electron microscopy (EM) at the single-cell level at defined intervals. We demonstrated the spatiotemporal expression of six major VZV proteins, ORF61, IE62, IE63, ORF29, ORF23, and gE, representing all putative kinetic classes, for the first time. Newly synthesized ORF61, as well as IE62, the major VZV transactivator, appeared within 1 h, and they were targeted to different subnuclear compartments. The formation of VZV DNA replication compartments started between 4 and 6 h, involved recruitment of ORF29 to putative IE62 prereplication sites, and resulted in large globular nuclear compartments where newly synthesized viral DNA accumulated. Although considered a late protein, gE accumulated in the Golgi compartment at as early as 4 h. ORF23 capsid protein was present at 9 h. The assembly of viral nucleocapsids and mature enveloped VZ virions was detected by 9 to 12 h by time-resolved EM. Although syncytium formation is a hallmark of VZV infection, infection of neighboring cells did not require cell-cell fusion; its occurrence from 9 h is likely to amplify VZV replication. Our results define the productive cycle of VZV infection in a single cell as occurring in 9 to 12 h.
Figures
References
-
- Asano, Y., and M. Takahashi. 1979. Studies on the polypeptides of varicella-zoster (V-Z) virus. 1. Detection of varicella-zoster virus polypeptides in infected cells. Biken J. 2281-89. - PubMed
-
- Asano, Y., and M. Takahashi. 1980. Studies on the polypeptides of varicella-zoster (V-Z) virus. II. Syntheses of viral polypeptides in infected cells. Biken J. 2395-106. - PubMed
-
- Baiker, A., C. Bagowski, H. Ito, M. Sommer, L. Zerboni, K. Fabel, J. Hay, W. Ruyechan, and A. M. Arvin. 2004. The immediate-early 63 protein of varicella-zoster virus: analysis of functional domains required for replication in vitro and for T-cell and skin tropism in the SCIDhu model in vivo. J. Virol. 781181-1194. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

