Efficient gene therapy-based method for the delivery of therapeutics to primate cortex
- PMID: 19193857
- PMCID: PMC2650169
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810682106
Efficient gene therapy-based method for the delivery of therapeutics to primate cortex
Abstract
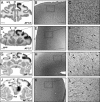
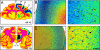
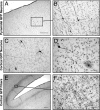
Transduction of the primate cortex with adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based gene therapy vectors has been challenging, because of the large size of the cortex. We report that a single infusion of AAV2 vector into thalamus results in widespread expression of transgene in the cortex through transduction of widely dispersed thalamocortical projections. This finding has important implications for the treatment of certain genetic and neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vite CH, et al. Effective gene therapy for an inherited CNS disease in a large animal model. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:355–364. - PubMed
-
- Vite CH, Passini MA, Haskins ME, Wolfe JH. Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated transduction in the cat brain. Gene Ther. 2003;10:1874–1881. - PubMed
-
- Kaplitt MG, et al. Safety and tolerability of gene therapy with an adeno-associated virus (AAV) borne GAD gene for Parkinson's disease: An open-label, phase I trial. Lancet. 2007;369:2097–2105. - PubMed
-
- Fiandaca M, Forsayeth J, Bankiewicz K. Current status of gene therapy trials for Parkinson's disease. Exp Neurol. 2008;209:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Eberling JL, et al. Results from a phase I safety trial of hAADC gene therapy for Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2008;70:1980–1983. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

