Glutamatergic regulation of serine racemase via reversal of PIP2 inhibition
- PMID: 19193859
- PMCID: PMC2635840
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0813105106
Glutamatergic regulation of serine racemase via reversal of PIP2 inhibition
Abstract
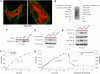
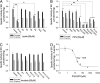
D-serine is a physiologic coagonist with glutamate at NMDA-subtype glutamate receptors. As D-serine is localized in glia, synaptically released glutamate presumably stimulates the glia to form and release D-serine, enabling glutamate/D-serine cotransmission. We show that serine racemase (SR), which generates D-serine from L-serine, is physiologically inhibited by phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2) presence in membranes where SR is localized. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR5) on glia leads to phospholipase C-mediated degradation of PIP2, relieving SR inhibition. Thus mutants of SR that cannot bind PIP2 lose their membrane localizations and display a 4-fold enhancement of catalytic activity. Moreover, mGluR5 activation of SR activity is abolished by inhibiting phospholipase C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Serine racemase regulated by binding to stargazin and PSD-95: potential N-methyl-D-aspartate-α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (NMDA-AMPA) glutamate neurotransmission cross-talk.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 24;289(43):29631-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.571604. Epub 2014 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25164819 Free PMC article.
-
Serine racemase: activation by glutamate neurotransmission via glutamate receptor interacting protein and mediation of neuronal migration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2105-10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409723102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15684087 Free PMC article.
-
Cofactors of serine racemase that physiologically stimulate the synthesis of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coagonist D-serine.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14542-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.222421299. Epub 2002 Oct 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12393813 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of human serine racemase, an emerging target for medicinal chemistry.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Jun;12(7):1037-55. doi: 10.2174/138945011795677755. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21291385 Review.
-
Serine racemase and the serine shuttle between neurons and astrocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Nov;1814(11):1558-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.01.001. Epub 2011 Jan 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21224019 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors regulating serine racemase and d-amino acid oxidase expression in the mouse striatum.Brain Res. 2021 Jan 15;1751:147202. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.147202. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33171153 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback inactivation of D-serine synthesis by NMDA receptor-elicited translocation of serine racemase to the membrane.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 5;106(18):7589-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809442106. Epub 2009 Apr 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19380732 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolytic flux controls D-serine synthesis through glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in astrocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):E2217-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1416117112. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25870284 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of the neuromodulator D-serine.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jul;67(14):2387-404. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0307-9. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20195697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serine racemase regulated by binding to stargazin and PSD-95: potential N-methyl-D-aspartate-α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (NMDA-AMPA) glutamate neurotransmission cross-talk.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 24;289(43):29631-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.571604. Epub 2014 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25164819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolosker H, Dumin E, Balan L, Foltyn VN. D-amino acids in the brain: D-serine in neurotransmission and neurodegeneration. FEBS J. 2008;275(14):3514–3526. - PubMed
-
- Oliet SH, Mothet JP. Molecular determinants of D-serine-mediated gliotransmission: from release to function. Glia. 2006;54(7):726–737. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Oka T, Takahashi K. Endogenous D-serine in rat brain: N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-related distribution and aging. J Neurochem. 1993;60(2):783–786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

