The serum response factor and a putative novel transcription factor regulate expression of the immediate-early gene Arc/Arg3.1 in neurons
- PMID: 19193899
- PMCID: PMC2874324
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5575-08.2009
The serum response factor and a putative novel transcription factor regulate expression of the immediate-early gene Arc/Arg3.1 in neurons
Abstract
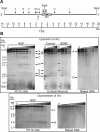
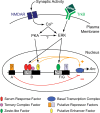
The immediate-early effector gene Arc/Arg3.1 is robustly upregulated by synaptic activity associated with learning and memory. Here we show in primary cortical neuron culture that diverse stimuli induce Arc expression through new transcription. Searching for regulatory regions important for Arc transcription, we found nine DNaseI-sensitive nucleosome-depleted sites at this genomic locus. A reporter gene encompassing these sites responded to synaptic activity in an NMDA receptor-dependent manner, consistent with endogenous Arc mRNA. Responsiveness mapped to two enhancer regions approximately 6.5 kb and approximately 1.4 kb upstream of Arc. We dissected these regions further and found that the proximal enhancer contains a functional and conserved "Zeste-like" response element that binds a putative novel nuclear protein in neurons. Therefore, activity regulates Arc transcription partly by a novel signaling pathway. We also found that the distal enhancer has a functional and highly conserved serum response element. This element binds serum response factor, which is recruited by synaptic activity to regulate Arc. Thus, Arc is the first target of serum response factor that functions at synapses to mediate plasticity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Involvement of SRF coactivator MKL2 in BDNF-mediated activation of the synaptic activity-responsive element in the Arc gene.J Neurochem. 2019 Jan;148(2):204-218. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14596. Epub 2018 Nov 12. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30244496
-
Characterization and Transcriptional Activation of the Immediate Early Gene ARC During a Neural Correlate of Classical Conditioning.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov;69(3):380-390. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01367-z. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31273643
-
Arc/Arg3.1 mRNA expression reveals a subcellular trace of prior sound exposure in adult primary auditory cortex.Neuroscience. 2011 May 5;181:117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.02.034. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21334422 Free PMC article.
-
The immediate early gene arc/arg3.1: regulation, mechanisms, and function.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 12;28(46):11760-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3864-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19005037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arc/Arg3.1: linking gene expression to synaptic plasticity and memory.Neuron. 2006 Nov 9;52(3):403-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.10.016. Neuron. 2006. PMID: 17088207 Review.
Cited by
-
Early phase of plasticity-related gene regulation and SRF dependent transcription in the hippocampus.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 23;8(7):e68078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068078. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23935853 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Egr1/zif268 to Activity-Dependent Arc/Arg3.1 Transcription in the Dentate Gyrus and Area CA1 of the Hippocampus.Front Behav Neurosci. 2011 Aug 17;5:48. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00048. eCollection 2011. Front Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21887136 Free PMC article.
-
The Arc of cognition: Signaling cascades regulating Arc and implications for cognitive function and disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 May;77:63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.09.023. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29559111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic treatment with the antipsychotic drug blonanserin modulates the responsiveness to acute stress with anatomical selectivity.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Jun;237(6):1783-1793. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05498-9. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32296859
-
Specific cytoarchitectureal changes in hippocampal subareas in daDREAM mice.Mol Brain. 2016 Feb 29;9:22. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0204-8. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 26928278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biggin MD, Bickel S, Benson M, Pirrotta V, Tjian R. Zeste encodes a sequence-specific transcription factor that activates the Ultrabithorax promoter in vitro. Cell. 1988;53:713–722. - PubMed
-
- Blaud M, Vossen C, Joseph G, Alazard R, Erard M, Nieto L. Characteristic patterns of N Oct-3 binding to a set of neuronal promoters. J Mol Biol. 2004;339:1049–1058. - PubMed
-
- Bode J, Goetze S, Heng H, Krawetz SA, Benham C. From DNA structure to gene expression: mediators of nuclear compartmentalization and dynamics. Chromosome Res. 2003;11:435–445. - PubMed
-
- Buchwalter G, Gross C, Wasylyk B. Ets ternary complex transcription factors. Gene. 2004;324:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
