Protein kinase Cepsilon inhibits UVR-induced expression of FADD, an adaptor protein, linked to both Fas- and TNFR1-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 19194472
- PMCID: PMC2854013
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2008.458
Protein kinase Cepsilon inhibits UVR-induced expression of FADD, an adaptor protein, linked to both Fas- and TNFR1-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
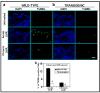
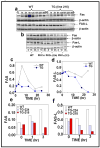
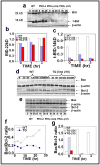
Protein kinase C (PKC)epsilon overexpression in FVB/N transgenic mice sensitized skin to UVR-induced development of squamous cell carcinomas and suppressed formation of sunburn cells, which are DNA-damaged keratinocytes undergoing apoptosis. Here, we elucidated the mechanisms associated with the inhibition of UVR-induced appearance of sunburn cells in PKCepsilon transgenic mice. We found that the inhibition of UVR-induced sunburn cell formation in PKCepsilon transgenic mice may be the result of the inhibition of the expression of Fas, Fas ligand, and the mammalian death adaptor protein termed Fas-associated with death domain (FADD). The adaptor protein FADD is the key component of the death-inducing signaling complex of both Fas and tumor necrosis factor receptor 1. A decreased expression of epidermal FADD was observed after a single UVR exposure. However, a complete loss of FADD expression was found after four (Monday, Wednesday, Friday, and Monday) repeated UVR exposures. FADD transmits apoptotic signals from death receptors to the downstream initiator caspase-8 and connects to the mitochondrial intrinsic apoptotic signal transduction pathway by the cleavage of Bid, a Bcl-2 family member. PKCepsilon-mediated loss of FADD expression inhibited UVR signals to the activation of both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures





Comment in
-
Protein kinase Cepsilon reveals importance of extrinsic apoptosis in preventing UV carcinogenesis.J Invest Dermatol. 2009 Aug;129(8):1853-6. doi: 10.1038/jid.2009.170. J Invest Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19603051
References
-
- Anonymous skin cancer; American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2008. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008.
-
- Kulms D, Düssmann H, Pöppelmann B, Ständer S, Schwarz A, Schwarz T. Apoptosis induced by disruption of the actin cytoskeleton is mediated via activation of CD95 (Fas/APO-1) Cell Death Differ. 2002;9:598–608. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–8. - PubMed
-
- Baud V, Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001;11:372–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

