Relapsing peritonitis caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patient: a case report
- PMID: 19194556
- PMCID: PMC2633208
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S215
Relapsing peritonitis caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patient: a case report
Abstract
Bordetella (B) bronchiseptica is a common veterinary pathogen, but has rarely been implicated in human infections. Most patients with B. bronchiseptica infections are compromised clinically such as in patients with a malignancy, AIDS, malnutrition, or chronic renal failure. We experienced a case of relapsing peritonitis caused by B. bronchiseptica associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). A 56-yr-old male, treated with CAPD due to end stage renal disease (ESRD), was admitted with complaints of abdominal pain and a turbid peritoneal dialysate. The culture of peritoneal dialysate identified B. bronchiseptica. The patient was treated with a combination of intraperitoneal antibiotics. There were two further episodes of relapsing peritonitis, although the organism was sensitive to the used antibiotics. Finally, the indwelling CAPD catheter was removed and the patient was started on hemodialysis. This is the first report of a B. bronchiseptica human infection in the Korean literature.
Keywords: Bordetella Bronchiseptica; Peritoneal Dialysis, Continuous Ambulatory; Peritonitis.
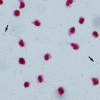
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica peritonitis associated with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):232-3. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.232-233.1981. J Clin Microbiol. 1981. PMID: 7276151 Free PMC article.
-
Relapsing peritonitis with Bacillus cereus in a patient on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Apr 26;2016:bcr2015212619. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2015-212619. BMJ Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27118739 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and pneumonia caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica.J Infect Dev Ctries. 2012 Jul 23;6(7):588-91. doi: 10.3855/jidc.2074. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2012. PMID: 22842947
-
Pet-related Pasteurella multocida induced peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: a case report and review of the literatures.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Mar 19;21(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-01765-1. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32192435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Peritoneal dialysis-related eosinophilic peritonitis: a case report and literature review].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018 Aug 18;50(4):747-751. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018. PMID: 30122784 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Isolation of Bordetella bronchiseptica from blood and a pancreatic abscess.J Clin Microbiol. 2015 May;53(5):1778-80. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00175-15. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25740781 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica in two HIV-positive patients.Sao Paulo Med J. 2016 May 13;134(3):268-72. doi: 10.1590/1516-3180.2015.02492701. Sao Paulo Med J. 2016. PMID: 27191248 Free PMC article.
-
Canine acquired pneumonia caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica.IDCases. 2023 Oct 31;34:e01922. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2023.e01922. eCollection 2023. IDCases. 2023. PMID: 37965382 Free PMC article.
-
Kitten-transmitted Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in a patient receiving temozolomide for glioblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2011 Apr;102(2):335-9. doi: 10.1007/s11060-010-0322-6. Epub 2010 Jul 30. J Neurooncol. 2011. PMID: 20676728
-
A real-time PCR assay with improved specificity for detection and discrimination of all clinically relevant Bordetella species by the presence and distribution of three Insertion Sequence elements.BMC Res Notes. 2011 Jan 21;4:11. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-11. BMC Res Notes. 2011. PMID: 21255383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amador C, Chiner E, Calpe JL, Ortiz de la Table V, Martinez C, Pasquau F. Pneumonia due to Bordetella bronchiseptica in a patient with AIDS. Rev Infect Dis. 1991;13:771–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

