The mildly elevated serum bilirubin level is negatively associated with the incidence of end stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 19194557
- PMCID: PMC2633177
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S22
The mildly elevated serum bilirubin level is negatively associated with the incidence of end stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy
Abstract
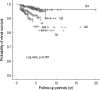
Oxidative stress plays various roles in the development and progression of IgA nephropathy, while bilirubin is known as a potent antioxidant. We therefore hypothesized that serum bilirubin would be associated with renal prognosis in IgA nephropathy. The study subjects comprised 1,458 adult patients with primary IgA nephropathy in Korea. We grouped patients according to the following quartile levels of bilirubin: <0.4 mg/dL (Q1), 0.4-0.5 mg/dL (Q2), 0.6-0.7 mg/dL (Q3), and >0.8 mg/dL (Q4). The outcome data were obtained from the Korean Registry of end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Eighty patients (5.5%) contracted ESRD during a mean follow-up period of 44.9 months. The ESRD incidences were 10.7% in Q1, 8.2% in Q2, 2.8% in Q3, and 2.8% in Q4 (p<0.001). The relative risk of ESRD compared to that in Q1 was 0.307 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.126-0.751) in Q3 and 0.315 (95% CI, 0.130-0.765) in Q4. The differences of ESRD incidence were greater in subgroups of males and of patients aged 35 yr or more, with serum albumin 4.0 g/dL or more, with normotension, with eGFR 60 mL/min/1.73 m(2) or more, and with proteinuria less then 3+ by dipstick test. In conclusion, higher bilirubin level was negatively associated with ESRD incidence in IgA nephropathy.
Keywords: Bilirubin; Glomerulonephritis, IGA; Kidney Failure, Chronic.
Figures
References
-
- Donadio JV, Grande JP. IgA nephropathy. New Engl J Med. 2002;347:738–748. - PubMed
-
- Barratt J, Feehally J. IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:2088–2097. - PubMed
-
- Descamps-Latscha B, Witko-Sarsat V, Nguyen-Khoa T, Nguyen AT, Gausson V, Mothu N, Cardoso C, Noel LH, Guerin AP, London GM, Jungers P. Early prediction of IgA nephropathy progression: proteinuria and AOPP are strong prognostic markers. Kidney Int. 2004;66:1606–1612. - PubMed
-
- Chen HC, Tomino Y, Yaguchi Y, Fukui M, Yokoyama K, Watanabe A, Koide H. Oxidative metabolism of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) in patients with IgA nephropathy. J Clin Lab Anal. 1992;6:35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous