Structural genomics is the largest contributor of novel structural leverage
- PMID: 19194785
- PMCID: PMC2705706
- DOI: 10.1007/s10969-008-9055-6
Structural genomics is the largest contributor of novel structural leverage
Abstract
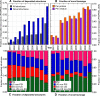
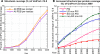
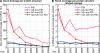
The Protein Structural Initiative (PSI) at the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) is funding four large-scale centers for structural genomics (SG). These centers systematically target many large families without structural coverage, as well as very large families with inadequate structural coverage. Here, we report a few simple metrics that demonstrate how successfully these efforts optimize structural coverage: while the PSI-2 (2005-now) contributed more than 8% of all structures deposited into the PDB, it contributed over 20% of all novel structures (i.e. structures for protein sequences with no structural representative in the PDB on the date of deposition). The structural coverage of the protein universe represented by today's UniProt (v12.8) has increased linearly from 1992 to 2008; structural genomics has contributed significantly to the maintenance of this growth rate. Success in increasing novel leverage (defined in Liu et al. in Nat Biotechnol 25:849-851, 2007) has resulted from systematic targeting of large families. PSI's per structure contribution to novel leverage was over 4-fold higher than that for non-PSI structural biology efforts during the past 8 years. If the success of the PSI continues, it may just take another approximately15 years to cover most sequences in the current UniProt database.
Figures
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/nar/gkm993', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm993'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC2238974', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2238974/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '18000004', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18000004/'}]}
- Andreeva A, Howorth D, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE, Hubbard TJ, Chothia C, Murzin AG (2008) Data growth and its impact on the SCOP database: new developments. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D419–D425. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm993 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/nar/gkh131', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh131'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC308865', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC308865/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '14681372', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14681372/'}]}
- Apweiler R, Bairoch A, Wu CH, Barker WC, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, Gasteiger E, Huang H, Lopez R, Magrane M et al (2004) UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D115–D119. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh131 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/j.str.2006.06.005', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2006.06.005'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16955948', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16955948/'}]}
- Berman HM, Burley SK, Chiu W, Sali A, Adzhubei A, Bourne PE, Bryant SH, Dunbrack RL Jr, Fidelis K, Frank J et al (2006) Outcome of a workshop on archiving structural models of biological macromolecules. Structure 14:1211–1217. doi:10.1016/j.str.2006.06.005 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1093/nar/gkl971', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl971'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1669775', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1669775/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17142228', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17142228/'}]}
- Berman H, Henrick K, Nakamura H, Markley JL (2007) The worldwide Protein Data Bank (wwPDB): ensuring a single, uniform archive of PDB data. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D301–D303. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl971 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

