Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by nanofibers
- PMID: 19196152
- PMCID: PMC2744836
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0227
Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by nanofibers
Abstract
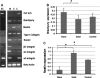
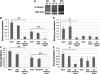
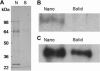
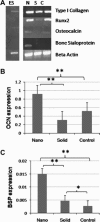
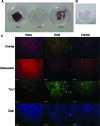
Controlled differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESC) is necessary to their use as a cell source for tissue engineering or regeneration. To date, most studies have concentrated on chemical cues to direct ESC differentiation. However, during normal embryonic development, multiple factors beyond chemical cues play a role, including the extracellular matrix (ECM) in bone development. In this study, we use nanofibrous (NF) matrices to mimic the morphology of the ECM to examine the contribution of the ECM morphology to the differentiation of mouse ESC. After 12 h of differentiation culture, mouse ESC form protrusions interacting with NF matrices, while they appear not to interact with flat films. Immunofluorescence staining after 26 days of differentiation culture indicates a greater degree of differentiation for mouse ESC on NF matrices compared to flat films. Polymerase chain reaction results, also, show greater degree of osteogenic differentiation on NF matrices compared to flat films when osteogenic supplements are added to the culture. Overall, these results demonstrate that NF morphology contributes to the controlled differentiation of mouse ESC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The influence of three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffolds on the osteogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells.Biomaterials. 2009 May;30(13):2516-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Jan 26. Biomaterials. 2009. PMID: 19176243 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous nitric oxide enhances calcification in embryonic stem cell-derived osteogenic cultures.Differentiation. 2015 Mar-Apr;89(3-4):97-103. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2015.02.001. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Differentiation. 2015. PMID: 25929821
-
The enhancement of human embryonic stem cell osteogenic differentiation with nano-fibrous scaffolding.Biomaterials. 2010 Jul;31(21):5526-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.065. Epub 2010 Apr 28. Biomaterials. 2010. PMID: 20430439 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of nanofibers on mesenchymal stem cells: environmental factors affecting cell adhesion and osteogenic differentiation and their mechanisms.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020 Nov.;21(11):871-884. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000355. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2020. PMID: 33150771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering the embryoid body microenvironment to direct embryonic stem cell differentiation.Biotechnol Prog. 2009 Jan-Feb;25(1):43-51. doi: 10.1002/btpr.139. Biotechnol Prog. 2009. PMID: 19198003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biomaterials and stem cells for tissue engineering.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013 Apr;13(4):527-40. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2013.756468. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23327471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of stem cell fate by engineering their micro and nanoenvironment.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Jan 26;7(1):37-50. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.37. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25621104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling, validation and verification of three-dimensional cell-scaffold contacts from terabyte-sized images.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Nov 28;18(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1928-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29183290 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells: understanding, creating, and exploiting the nano-niche for regenerative medicine.ACS Nano. 2013 Mar 26;7(3):1867-81. doi: 10.1021/nn3037094. Epub 2013 Feb 15. ACS Nano. 2013. PMID: 23414366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial pattern dynamics of 3D stem cell loss of pluripotency via rules-based computational modeling.PLoS Comput Biol. 2013;9(3):e1002952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002952. Epub 2013 Mar 14. PLoS Comput Biol. 2013. PMID: 23516345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Evans M.J. Kaufman M.H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154. - PubMed
-
- McCloskey K. Gilroy M. Nerem R. Use of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells as a cell source to generate vessel structures in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:497. - PubMed
-
- Ke Q. Yang Y. Rana J. Yu C. Morgan J. Yong-Fu X. Embryonic stem cells cultured in biodegradable scaffold repair infarcted myocardium in mice. Acta Physiologica Sinica. 2005;57:673. - PubMed

