Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by nanofibers
- PMID: 19196152
- PMCID: PMC2744836
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0227
Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by nanofibers
Abstract
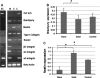
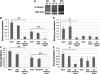
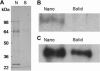
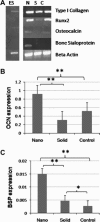
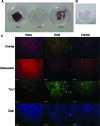
Controlled differentiation of embryonic stem cells (ESC) is necessary to their use as a cell source for tissue engineering or regeneration. To date, most studies have concentrated on chemical cues to direct ESC differentiation. However, during normal embryonic development, multiple factors beyond chemical cues play a role, including the extracellular matrix (ECM) in bone development. In this study, we use nanofibrous (NF) matrices to mimic the morphology of the ECM to examine the contribution of the ECM morphology to the differentiation of mouse ESC. After 12 h of differentiation culture, mouse ESC form protrusions interacting with NF matrices, while they appear not to interact with flat films. Immunofluorescence staining after 26 days of differentiation culture indicates a greater degree of differentiation for mouse ESC on NF matrices compared to flat films. Polymerase chain reaction results, also, show greater degree of osteogenic differentiation on NF matrices compared to flat films when osteogenic supplements are added to the culture. Overall, these results demonstrate that NF morphology contributes to the controlled differentiation of mouse ESC.
Figures

References
-
- Evans M.J. Kaufman M.H. Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos. Nature. 1981;292:154. - PubMed
-
- McCloskey K. Gilroy M. Nerem R. Use of embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells as a cell source to generate vessel structures in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:497. - PubMed
-
- Ke Q. Yang Y. Rana J. Yu C. Morgan J. Yong-Fu X. Embryonic stem cells cultured in biodegradable scaffold repair infarcted myocardium in mice. Acta Physiologica Sinica. 2005;57:673. - PubMed

