Post-translational import of protein into the endoplasmic reticulum of a trypanosome: an in vitro system for discovery of anti-trypanosomal chemical entities
- PMID: 19196237
- PMCID: PMC2769561
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20081787
Post-translational import of protein into the endoplasmic reticulum of a trypanosome: an in vitro system for discovery of anti-trypanosomal chemical entities
Abstract
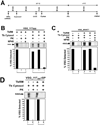
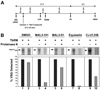
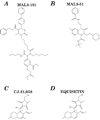
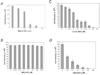
HAT (human African trypanosomiasis), caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei, is an emerging disease for which new drugs are needed. Expression of plasma membrane proteins [e.g. VSG (variant surface glycoprotein)] is crucial for the establishment and maintenance of an infection by T. brucei. Transport of a majority of proteins to the plasma membrane involves their translocation into the ER (endoplasmic reticulum). Thus inhibition of protein import into the ER of T. brucei would be a logical target for discovery of lead compounds against trypanosomes. We have developed a TbRM (T. brucei microsome) system that imports VSG_117 post-translationally. Using this system, MAL3-101, equisetin and CJ-21,058 were discovered to be small molecule inhibitors of VSG_117 translocation into the ER. These agents also killed bloodstream T. brucei in vitro; the concentrations at which 50% of parasites were killed (IC50) were 1.5 microM (MAL3-101), 3.3 microM (equisetin) and 7 microM (CJ-21,058). Thus VSG_117 import into TbRMs is a rapid and novel assay to identify 'new chemical entities' (e.g. MAL3-101, equisetin and CJ-21,058) for anti-trypanosome drug development.
Figures


Comment in
-
Drug screening by crossing membranes: a novel approach to identification of trypanocides.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 15;419(2):e1-3. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090283. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19309311
References
-
- Renslo AR, McKerrow JH. Drug discovery and development for neglected parasitic diseases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006;2:701–710. - PubMed
-
- Wickner W, Schekman R. Protein translocation across biological membranes. Science. 2005;310:1452–1456. - PubMed
-
- Albers SV, Szabo Z, Driessen AJ. Protein secretion in the Archaea: multiple paths towards a unique cell surface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006;4:537–547. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Liang XH, Uliel S, Unger R, Ullu E, Michaeli S. RNA interference of signal peptide-binding protein SRP54 elicits deleterious effects and protein sorting defects in trypanosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:47348–47357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

