SISCAPA peptide enrichment on magnetic beads using an in-line bead trap device
- PMID: 19196707
- PMCID: PMC2689780
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M800446-MCP200
SISCAPA peptide enrichment on magnetic beads using an in-line bead trap device
Abstract
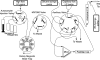
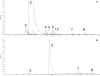
A SISCAPA (stable isotope standards and capture by anti-peptide antibodies) method for specific antibody-based capture of individual tryptic peptides from a digest of whole human plasma was developed using a simplified magnetic bead protocol and a novel rotary magnetic bead trap device. Following off-line equilibrium binding of peptides by antibodies and subsequent capture of the antibodies on magnetic beads, the bead trap permitted washing of the beads and elution of bound peptides inside a 150-microm-inner diameter capillary that forms part of a nanoflow LC-MS/MS system. The bead trap sweeps beads against the direction of liquid flow using a continuous succession of moving high magnetic field-gradient trap regions while mixing the beads with the flowing liquid. This approach prevents loss of low abundance captured peptides and allows automated processing of a series of SISCAPA reactions. Selected tryptic peptides of alpha(1)-antichymotrypsin and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein were enriched relative to a high abundance serum albumin peptide by 1,800 and 18,000-fold, respectively, as measured by multiple reaction monitoring. A large majority of the peptides that are bound nonspecifically in SISCAPA reactions were shown to bind to components other than the antibody (e.g. the magnetic beads), suggesting that substantial improvement in enrichment could be achieved by development of improved inert bead surfaces.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson, L., and Hunter, C. L. ( 2006) Quantitative mass spectrometric multiple reaction monitoring assays for major plasma proteins. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 5, 573–588 - PubMed
-
- Pieper, R., Su, Q., Gatlin, C. L., Huang, S. T., Anderson, N. L., and Steiner, S. ( 2003) Multi-component immunoaffinity subtraction chromatography: an innovative step towards a comprehensive survey of the human plasma proteome. Proteomics 3, 422–432 - PubMed
-
- Anderson, N. L., Anderson, N. G., Haines, L. R., Hardie, D. B., Olafson, R. W., and Pearson, T. W. ( 2004) Mass spectrometric quantitation of peptides and proteins using stable isotope standards and capture by anti-peptide antibodies (SISCAPA). J. Proteome Res. 3, 235–244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

