GPCR and G proteins: drug efficacy and activation in live cells
- PMID: 19196832
- PMCID: PMC5419261
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0204
GPCR and G proteins: drug efficacy and activation in live cells
Abstract
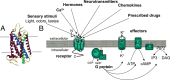
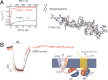
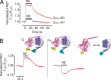
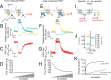
Many biochemical pathways are driven by G protein-coupled receptors, cell surface proteins that convert the binding of extracellular chemical, sensory, and mechanical stimuli into cellular signals. Their interaction with various ligands triggers receptor activation that typically couples to and activates heterotrimeric G proteins, which in turn control the propagation of secondary messenger molecules (e.g. cAMP) involved in critically important physiological processes (e.g. heart beat). Successful transfer of information from ligand binding events to intracellular signaling cascades involves a dynamic interplay between ligands, receptors, and G proteins. The development of Förster resonance energy transfer and bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based methods has now permitted the kinetic analysis of initial steps involved in G protein-coupled receptor-mediated signaling in live cells and in systems as diverse as neurotransmitter and hormone signaling. The direct measurement of ligand efficacy at the level of the receptor by Förster resonance energy transfer is also now possible and allows intrinsic efficacies of clinical drugs to be linked with the effect of receptor polymorphisms.
Figures


References
-
- Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T, Behnke CA, Motoshima H, Fox BA, Le Trong I, Teller DC, Okada T, Stenkamp RE, Yamamoto M, Miyano M2000. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: a G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289:739–745 - PubMed
-
- Rosenbaum DM, Cherezov V, Hanson MA, Rasmussen SG, Thian FS, Kobilka TS, Choi HJ, Yao XJ, Weis WI, Stevens RC, Kobilka BK GPCR engineering yields high-resolution structural insights into β2-adrenergic receptor function. Science 318:1266–1273 - PubMed
-
- Bourne HR, Sanders DA, McCormick F1991. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature 349:117–127 - PubMed
-
- Wettschureck N, Offermanns S2005. Mammalian G proteins and their cell type specific functions. Physiol Rev 85:1159–1204 - PubMed
-
- Tao YX2006. Inactivating mutations of G protein-coupled receptors and diseases: structure-function insights and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther 111:949–973 - PubMed

