A mouse forward genetics screen identifies LISTERIN as an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in neurodegeneration
- PMID: 19196968
- PMCID: PMC2650114
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812819106
A mouse forward genetics screen identifies LISTERIN as an E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in neurodegeneration
Abstract
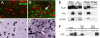
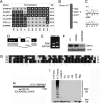
A mouse neurological mutant, lister, was identified through a genome-wide N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenesis screen. Homozygous lister mice exhibit profound early-onset and progressive neurological and motor dysfunction. lister encodes a RING finger protein, LISTERIN, which functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase in vitro. Although lister is widely expressed in all tissues, motor and sensory neurons and neuronal processes in the brainstem and spinal cord are primarily affected in the mutant. Pathological signs include gliosis, dystrophic neurites, vacuolated mitochondria, and accumulation of soluble hyperphosphorylated tau. Analysis with a different lister allele generated through targeted gene trap insertion reveals LISTERIN is required for embryonic development and confirms that direct perturbation of a LISTERIN-regulated process causes neurodegeneration. The lister mouse uncovers a pathway involved in neurodegeneration and may serves as a model for understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying human neurodegenerative disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Singleton AB, et al. Alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson's disease. Science. 2003;302:841. - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG, et al. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature. 1997;388:839–840. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Zarranz JJ, et al. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:164–173. - PubMed
-
- Farrer MJ. Genetics of Parkinson disease: Paradigm shifts and future prospects. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:306–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

