Elongation dynamics shape bursty transcription and translation
- PMID: 19196995
- PMCID: PMC2650307
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803507106
Elongation dynamics shape bursty transcription and translation
Abstract
Cells in isogenic populations may differ substantially in their molecular make up because of the stochastic nature of molecular processes. Stochastic bursts in process activity have a great potential for generating molecular noise. They are characterized by (short) periods of high process activity followed by (long) periods of process silence causing different cells to experience activity periods varying in size, duration, and timing. We present an analytically solvable model of bursts in molecular networks, originally developed for the analysis of telecommunication networks. We define general measures for model-independent characterization of bursts (burst size, significance, and duration) from stochastic time series. Inspired by the discovery of bursts in mRNA and protein production by others, we use those indices to investigate the role of stochastic motion of motor proteins along biopolymer chains in determining burst properties. Collisions between neighboring motor proteins can attenuate bursts introduced at the initiation site on the chain. Pausing of motor proteins can give rise to bursts. We investigate how these effects are modulated by the length of the biopolymer chain and the kinetic properties of motion. We discuss the consequences of those results for transcription and translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

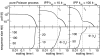






References
-
- Elowitz MB, Levine AJ, Siggia ED, Swain PS. Stochastic gene expression in a single cell. Science. 2002;297:1183–1186. - PubMed
-
- Ozbudak EM, Thattai M, Kurtser I, Grossman AD, van Oudenaarden A. Regulation of noise in the expression of a single gene. Nat Genet. 2002;31:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Golding I, Paulsson J, Zawilski SM, Cox EC. Real-time kinetics of gene activity in individual bacteria. Cell. 2005;123:1025–1036. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Xiao J, Ren X, Lao K, Xie XS. Probing gene expression in live cells, one protein molecule at a time. Science. 2006;311:1600–1603. - PubMed
-
- Kærn M, Elston TC, Blake WJ, Collins JJ. Stochasticity in gene expression: From theories to phenotypes. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6:451–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

