Smooth muscle cells give rise to osteochondrogenic precursors and chondrocytes in calcifying arteries
- PMID: 19197075
- PMCID: PMC2716055
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.183053
Smooth muscle cells give rise to osteochondrogenic precursors and chondrocytes in calcifying arteries
Abstract
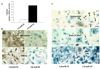
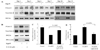
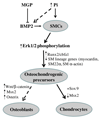
Vascular calcification is a major risk factor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. To develop appropriate prevention and/or therapeutic strategies for vascular calcification, it is important to understand the origins of the cells that participate in this process. In this report, we used the SM22-Cre recombinase and Rosa26-LacZ alleles to genetically trace cells derived from smooth muscle. We found that smooth muscle cells (SMCs) gave rise to osteochondrogenic precursor- and chondrocyte-like cells in calcified blood vessels of matrix Gla protein deficient (MGP(-/-)) mice. This lineage reprogramming of SMCs occurred before calcium deposition and was associated with an early onset of Runx2/Cbfa1 expression and the downregulation of myocardin and Msx2. There was no change in the constitutive expression of Sox9 or bone morphogenetic protein 2. Osterix, Wnt3a, and Wnt7a mRNAs were not detected in either calcified MGP(-/-) or noncalcified wild-type (MGP(+/+)) vessels. Finally, mechanistic studies in vitro suggest that Erk signaling might be required for SMC transdifferentiation under calcifying conditions. These results provide strong support for the hypothesis that adult SMCs can transdifferentiate and that SMC transdifferentiation is an important process driving vascular calcification and the appearance of skeletal elements in calcified vascular lesions.
Figures
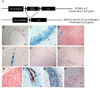

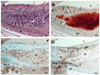
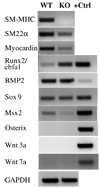
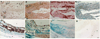
Comment in
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification.Circ Res. 2009 Mar 27;104(6):710-1. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.195487. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19325156 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rutsch F, Ruf N, Vaingankar S, Toliat MR, Suk A, Hohne W, Schauer G, Lehmann M, Roscioli T, Schnabel D, Epplen JT, Knisely A, Superti-Furga A, McGill J, Filippone M, Sinaiko AR, Vallance H, Hinrichs B, Smith W, Ferre M, Terkeltaub R, Nurnberg P. Mutations in ENPP1 are associated with 'idiopathic' infantile arterial calcification. Nat Genet. 2003;34:379–381. - PubMed
-
- Block GA. Control of serum phosphorus: implications for coronary artery calcification and calcific uremic arteriolopathy (calciphylaxis) Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2001;10:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Taylor AJ, Burke AP, O'Malley PG, Farb A, Malcom GT, Smialek J, Virmani R. A comparison of the Framingham risk index, coronary artery calcification, and culprit plaque morphology in sudden cardiac death. Circulation. 2000;101:1243–1248. - PubMed
-
- Shanahan CM, Cary NR, Salisbury JR, Proudfoot D, Weissberg PL, Edmonds ME. Medial localization of mineralization-regulating proteins in association with Monckeberg’s sclerosis: evidence for smooth muscle cell-mediated vascular calcification. Circulation. 1999;100:2168–2176. - PubMed
-
- Moe SM, O'Neill KD, Duan D, Ahmed S, Chen NX, Leapman SB, Fineberg N, Kopecky K. Medial artery calcification in ESRD patients is associated with deposition of bone matrix proteins. Kidney Int. 2002;61:638–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

