Spectral measurements of large particles by flow cytometry
- PMID: 19199345
- PMCID: PMC2674113
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.a.20706
Spectral measurements of large particles by flow cytometry
Abstract
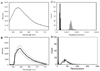
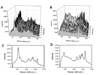
Flow cytometers designed to analyze large particles are enabling new applications in biology and chemistry. Similarly, flow spectroscopy approaches are extending the capabilities of the flow cytometry platform. Here, we report on the adaptation of a commercial large particle analyzer to measure fluorescence and Raman spectra of individual particles at high speeds. We modified a Union Biometrica COPAS Plus instrument to allow red excitation and optical fiber-based light collection and spectral analysis using a spectrograph and CCD array detector. These modifications did not compromise the ability of the instrument to resolve different sized particles based on their extinction and time of flight signals. The modified instrument has the sensitivity and spectral resolution to measure the fluorescence and Raman signals from individual particles with signal integration times of 10 usec. The high speed spectral analysis of individual particles in flow will enable new applications in biological and chemical analyses.
(c) 2009 International Society for Advancement of Cytometry.
Figures
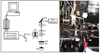

References
-
- Couillault C, Pujol N, Reboul J, Sabatier L, Guichou JF, Kohara Y, Ewbank JJ. tlr-independent control of innate immunity in caenorhabditis elegans by the tir domain adaptor protein tir-1, an ortholog of human sarm. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:488–494. - PubMed
-
- Hertweck M, Baumeister R. automated assays to study longevity in c. elegans. Mech Ageing Dev. 2005;126:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez LA, Hatch EW, Armann B, Odorico JS, Hullett DA, Sollinger HW, Hanson MS. validation of large particle flow cytometry for the analysis and sorting of intact pancreatic islets. Transplantation. 2005;80:729–737. - PubMed
-
- Dixon S, Ziebart KT, He Z, Jeddeloh M, Yoo CL, Wang X, Lehman A, Lam KS, Toney MD, Kurth MJ. aminodeoxychorismate synthase inhibitors from one-bead one-compound combinatorial libraries: "staged" inhibitor design. J Med Chem. 2006;49:7413–7426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

