Proteomic analysis of human parotid gland exosomes by multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT)
- PMID: 19199708
- PMCID: PMC2693447
- DOI: 10.1021/pr800658c
Proteomic analysis of human parotid gland exosomes by multidimensional protein identification technology (MudPIT)
Abstract
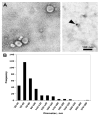
Human ductal saliva contributes over a thousand unique proteins to whole oral fluids. The mechanism by which most of these proteins are secreted by salivary glands remains to be determined. The present study used a mass spectrometry-based, shotgun proteomics approach to explore the possibility that a subset of the proteins found in saliva are derived from exosomes, membrane-bound vesicles of endosomal origin within multivesicular endosomes. Using MudPIT (multidimensional protein identification technology) mass spectrometry, we catalogued 491 proteins in the exosome fraction of human parotid saliva. Many of these proteins were previously observed in ductal saliva from parotid glands (265 proteins). Furthermore, 72 of the proteins in parotid exosomes overlap with those previously identified as urinary exosome proteins, proteins which are also frequently associated with exosomes from other tissues and cell types. Gene Ontology (GO) and KEGG pathway analyses found that cytosolic proteins comprise the largest category of proteins in parotid exosomes (43%), involved in such processes as phosphatidylinositol signaling system, calcium signaling pathway, inositol metabolism, protein export, and signal transduction, among others; whereas the integral plasma membrane proteins and associated/peripheral plasma membrane proteins (26%) were associated with extracellular matrix-receptor interaction, epithelial cell signaling, T-cell and B-cell receptor signaling, cytokine receptor interaction, and antigen processing and presentation, among other biological functions. In addition, these putative saliva exosomal proteins were linked to specific diseases (e.g., neurodegenerative disorders, prion disease, cancers, type I and II diabetes). Consequently, parotid glands secrete exosomes that reflect the metabolic and functional status of the gland and may also carry informative protein markers useful in the diagnosis and treatment of systemic diseases.
Figures





References
-
- Bennick A. J Oral Biosci. 2007;49:24–26.
-
- Denny P, Hagen FK, Hardt M, Liao L, Yan W, Arellanno M, Bassilian S, Bedi GS, Boontheung P, Cociorva D, Delahunty CM, Denny T, Dunsmore J, Faull KF, Gilligan J, Gonzalez-Begne M, Halgand F, Hall SC, Han X, Henson B, Hewel J, Hu S, Jeffrey S, Jiang J, Loo JA, Ogorzalek Loo RR, Malamud D, Melvin JE, Miroshnychenko O, Navazesh M, Niles R, Park SK, Prakobphol A, Ramachandran P, Richert M, Robinson S, Sondej M, Souda P, Sullivan MA, Takashima J, Than S, Wang J, Whitelegge JP, Witkowska HE, Wolinsky L, Xie Y, Xu T, Yu W, Ytterberg J, Wong DT, Yates JR, 3rd, Fisher SJ. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:1994–2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oppenheim FG, Salih E, Siqueira WL, Zhang W, Helmerhorst EJ. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1098:22–50. - PubMed
-
- Tabak LA. Pediatr Dent. 2006;28:110–117. discussion 192–118. - PubMed
-
- Vitorino R, Lobo MJ, Ferrer-Correira AJ, Dubin JR, Tomer KB, Domingues PM, Amado FM. Proteomics. 2004;4:1109–1115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

