Anesthesia, calcium homeostasis and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19199872
- PMCID: PMC2735723
- DOI: 10.2174/156720509787313934
Anesthesia, calcium homeostasis and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
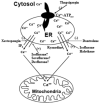
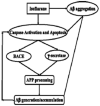
While anesthetics are indispensable clinical tools generally safe and effective, in some situations there is grown concern about selective neurotoxicity of these agents; the clinical significance is unclear as of yet. The mechanisms for inhalational anesthetics mediated cell damage are still not clear, although a role for calcium dysregulation has been suggested. For example, the inhaled anesthetic isoflurane decreases endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium concentration and increases that in the cytosol and mitochondria. Inhibition of ER calcium release, via either IP(3) or ryanodine receptors, significantly inhibited isoflurane neurotoxicity. Neurons made vulnerable to calcium dysregulation by overexpression of mutated presenilin-1 (PS1) or huntingtin (Q-111) proteins showed enhanced apoptosis upon isoflurane exposure. Sevoflurane and desflurane were less potent than isoflurane in altering intracellular calcium, and produced less apoptosis. Short exposures to inhalational anesthetics may provide neuroprotection by preconditioning via a sublethal stress, while prolonged exposures to inhalational anesthetics may induce cell damage by apoptosis through direct cytotoxic effects.
Figures
References
-
- Xie Z, Tanzi RE. Alzheimer’s disease and post-operative cognitive dysfunction. Exp Gerontol. 2006;41:346–359. - PubMed
-
- Culley DJ, Xie Z, Crosby G. General anesthetic-induced neurotoxicity: an emerging problem for the young and old? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2007;20:408–413. - PubMed
-
- Fodale V, Quattrone D, Trecroci C, Caminiti V, Santamaria LB. Alzheimer’s disease and anaesthesia: implications for the central cholinergic system. Br J Anaesth. 2006;97:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Wise-Faberowski L, Zhang H, Ing R, Pearlstein RD, Warner DS. Isoflurane-induced neuronal degeneration: an evaluation in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:651–657. - PubMed
-
- Wei HF, Liang G, Yang H, Wang QJ, Hawkins B, Madesh M, et al. The common inhalational anesthetic isoflurane induces apoptosis via activation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. Anesthesiology. 2008;108:251–260. - PubMed

