Neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing projection neurons in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord have synaptic AMPA receptors that contain GluR2, GluR3 and GluR4 subunits
- PMID: 19200070
- PMCID: PMC2695158
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06633.x
Neurokinin 1 receptor-expressing projection neurons in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord have synaptic AMPA receptors that contain GluR2, GluR3 and GluR4 subunits
Abstract
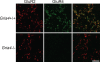
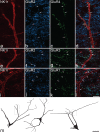
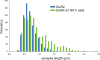
alpha-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors (AMPArs), which mediate fast excitatory glutamatergic transmission, are tetramers made from four subunits (GluR1-4 or GluRA-D). Although synaptic AMPArs are not normally detected by immunocytochemistry in perfusion-fixed tissue, they can be revealed by using antigen retrieval with pepsin. All AMPAr-positive synapses in spinal cord are thought to contain GluR2, while the other subunits have specific laminar distributions. GluR4 can be alternatively spliced such that it has a long or short cytoplasmic tail. We have reported that <10% of AMPAr-containing synapses in lamina II have the long form of GluR4, and that these are often arranged in dorsoventrally orientated clusters. In this study, we test the hypothesis that GluR4-containing receptors are associated with dorsal dendrites of projection neurons in laminae III and IV that express the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1r). Immunostaining for NK1r was carried out before antigen retrieval, and sections were then reacted to reveal GluR2 and either GluR4 (long form), GluR3 or GluR1. All NK1r-positive lamina III/IV neurons had numerous GluR2-immunoreactive puncta in their dendritic plasma membranes, and virtually all (97%) of the puncta tested were labelled (usually strongly) with the GluR4 antibody. Sizes of puncta varied, but many were elongated and they were significantly larger than nearby puncta that were not associated with the NK1r cells. None of the GluR2 puncta on these cells was positive for GluR1, while 85% were GluR3-immunoreactive. These results show that synaptic AMPArs on the dendrites of the lamina III/IV NK1r projection neurons contain GluR2, GluR3 and GluR4, but not GluR1 subunits.
Figures
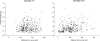
References
-
- Alvarez FJ, Dewey DE, Harrington DA, Fyffe REW. Cell-type specific organization of glycine receptor clusters in the mammalian spinal cord. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997;379:150–170. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez FJ, Villalba RM, Zerda R, Schneider SP. Vesicular glutamate transporters in the spinal cord, with special reference to sensory primary afferent synapses. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004;472:257–280. - PubMed
-
- Bleazard L, Hill RG, Morris R. The correlation between the distribution of the NK1 receptor and the actions of tachykinin agonists in the dorsal horn of the rat indicates that substance P does not have a functional role on substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) neurons. J. Neurosci. 1994;14:7655–7664. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

