A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals
- PMID: 19200528
- PMCID: PMC2668004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.005
A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals
Abstract
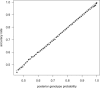
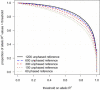
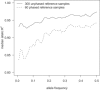
We present methods for imputing data for ungenotyped markers and for inferring haplotype phase in large data sets of unrelated individuals and parent-offspring trios. Our methods make use of known haplotype phase when it is available, and our methods are computationally efficient so that the full information in large reference panels with thousands of individuals is utilized. We demonstrate that substantial gains in imputation accuracy accrue with increasingly large reference panel sizes, particularly when imputing low-frequency variants, and that unphased reference panels can provide highly accurate genotype imputation. We place our methodology in a unified framework that enables the simultaneous use of unphased and phased data from trios and unrelated individuals in a single analysis. For unrelated individuals, our imputation methods produce well-calibrated posterior genotype probabilities and highly accurate allele-frequency estimates. For trios, our haplotype-inference method is four orders of magnitude faster than the gold-standard PHASE program and has excellent accuracy. Our methods enable genotype imputation to be performed with unphased trio or unrelated reference panels, thus accounting for haplotype-phase uncertainty in the reference panel. We present a useful measure of imputation accuracy, allelic R(2), and show that this measure can be estimated accurately from posterior genotype probabilities. Our methods are implemented in version 3.0 of the BEAGLE software package.
Figures


References
-
- Zeggini E., Scott L.J., Saxena R., Voight B.F., Marchini J.L., Hu T., de Bakker P.I., Abecasis G.R., Almgren P., Andersen G. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data and large-scale replication identifies additional susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:638–645. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

