Optimal timing of inner cell mass isolation increases the efficiency of human embryonic stem cell derivation and allows generation of sibling cell lines
- PMID: 19200798
- PMCID: PMC3335201
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.12.001
Optimal timing of inner cell mass isolation increases the efficiency of human embryonic stem cell derivation and allows generation of sibling cell lines
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
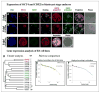
Figures
References
-
- Akutsu H, Cowan CA, Melton D. Human embryonic stem cells. Methods Enzymol. 2006;418:78–92. - PubMed
-
- Anderson S, Bankier AT, Barrell BG, de Bruijn MH, Coulson AR, Drouin J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981;290:457–465. - PubMed
-
- Baharvand H, Ashtiani SK, Valojerdi MR, Shahverdi A, Taee A, Sabour D. Establishment and in vitro differentiation of a new embryonic stem cell line from human blastocyst. Differentiation. 2004;72:224–229. - PubMed
-
- Bongso A, Fong CY, Ng SC, Ratnam S. Isolation and culture of inner cell mass cells from human blastocysts. Hum Reprod. 1994;9:2110–2117. - PubMed
-
- Brons IG, Smithers LE, Trotter MW, Rugg-Gunn P, Sun B, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Howlett SK, Clarkson A, Ahrlund-Richter L, Pedersen RA, et al. Derivation of pluripotent epiblast stem cells from mammalian embryos. Nature. 2007;448:191–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

