Cell-type specific regulation of gene expression by simian virus 40 T antigens
- PMID: 19201438
- PMCID: PMC2737743
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.12.038
Cell-type specific regulation of gene expression by simian virus 40 T antigens
Abstract
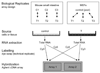
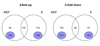
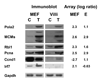
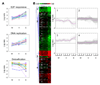
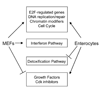
SV40 transforms cells through the action of two oncoproteins, large T antigen and small t antigen. Small t antigen targets phosphatase PP2A, while large T antigen stimulates cell proliferation and survival by action on multiple proteins, including the tumor suppressors Rb and p53. Large T antigen also binds components of the transcription initiation complex and several transcription factors. We examined global gene expression in SV40-transformed mouse embryo fibroblasts, and in enterocytes obtained from transgenic mice. SV40 transformation alters the expression of approximately 800 cellular genes in both systems. Much of this regulation is observed in both MEFs and enterocytes and is consistent with T antigen action on the Rb-E2F pathway. However, the regulation of many genes is cell-type specific, suggesting that unique signaling pathways are activated in different cell types upon transformation, and that the consequences of SV40 transformation depends on the type of cell targeted.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SV40 large T antigen targets multiple cellular pathways to elicit cellular transformation.Oncogene. 2005 Nov 21;24(52):7729-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209046. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16299533 Review.
-
Intestinal hyperplasia induced by simian virus 40 large tumor antigen requires E2F2.J Virol. 2007 Dec;81(23):13191-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01658-07. Epub 2007 Sep 12. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17855529 Free PMC article.
-
Simian virus 40 T-antigen-mediated gene regulation in enterocytes is controlled primarily by the Rb-E2F pathway.J Virol. 2009 Sep;83(18):9521-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00583-09. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19570859 Free PMC article.
-
Enterocyte proliferation and intestinal hyperplasia induced by simian virus 40 T antigen require a functional J domain.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):9481-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00922-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17581980 Free PMC article.
-
SV40 large T antigen functions in DNA replication and transformation.Adv Virus Res. 2000;55:75-134. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(00)55002-7. Adv Virus Res. 2000. PMID: 11050941 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Checkpoint inhibitor blockade and epigenetic reprogrammability in CD8+ T-cell activation and exhaustion.Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020 Mar 13;8:2515135520904238. doi: 10.1177/2515135520904238. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32206744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GnRH receptor activation competes at a low level with growth signaling in stably transfected human breast cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2011 Nov 3;11:476. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-476. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22051164 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the Ggamma-globin-Tag transgenic mouse model of hormone refractory prostate cancer: comparison to human prostate cancer.Prostate. 2010 May 1;70(6):630-45. doi: 10.1002/pros.21097. Prostate. 2010. PMID: 20058236 Free PMC article.
-
Conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell lines established from urine.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):F557-67. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00509.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19955187 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of a small C-terminal region of JCV and SV40 large T antigens has differential effects on transformation.Virology. 2014 Nov;468-470:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.07.038. Epub 2014 Aug 16. Virology. 2014. PMID: 25129438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahuja D, Saenz-Robles MT, Pipas JM. SV40 large T antigen targets multiple cellular pathways to elicit cellular transformation. Oncogene. 2005;24(52):7729–7745. - PubMed
-
- Baserga R, Ide T, Whelly S. Stimulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis in isolated nuclei and nucleoli by partially purified preparations of SV40 T antigen. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):685–691. - PubMed
-
- Churchill GA. Fundamentals of experimental design for cDNA microarrays. Nat Genet. 2002;32(Suppl):490–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

